Flk-2 is a marker in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation: a simple method to isolate long-term stem cells
- PMID: 11724967
- PMCID: PMC64718
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261562798
Flk-2 is a marker in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation: a simple method to isolate long-term stem cells
Abstract
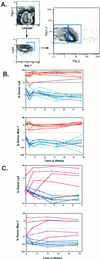
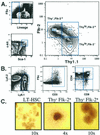
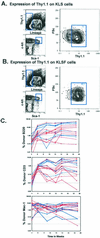
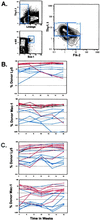
Clonogenic multipotent mouse hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and progenitor cells are contained within the c-kit(+) (K) lineage(-/lo) (L) Sca-1(+) (S) population of hematopoietic cells; long-term (LT) and short-term (ST) HSCs are Thy-1.1(lo). c-kit is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family, a class of receptors that are important in the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic cells. To establish whether the Flk-2/Flt3 receptor tyrosine kinase was expressed on the most primitive LT-HSCs, we sorted highly purified multipotent stem and progenitor cells on the basis of Flk-2 surface expression and used them in competitive reconstitution assays. Low numbers of Flk-2(-) HSCs gave rise to long-term multilineage reconstitution in the majority of recipients, whereas the transfer of Flk-2(+) multipotent cells resulted in mostly short-term multilineage reconstitution. The KLS subset of adult mouse bone marrow was analyzed for Flk-2 and Thy-1.1 expression. Three phenotypically and functionally distinct populations were isolated: Thy(lo) Flk-2(-) (LT-HSCs), Thy(lo) Flk-2(+) (ST-HSCs), and Thy(-) Flk-2(+) multipotent progenitors. The loss of Thy-1.1 and gain of Flk-2 expression marks the loss of self-renewal in HSC maturation. The addition of Flk-2 antibody to the lineage mix allows direct isolation of LT-HSC from adult bone marrow as c-kit(+) lin(-) Sca-1(+) Flk-2(-) from many strains of mice. Fetal liver HSCs are contained within Flk-2(-) and Flk-2(+) KTLS cells.
Figures
References
-
- Jones R J, Wagner J E, Celano P, Zicha M S, Sharkis S J. Nature (London) 1990;347:188–189. - PubMed
-
- Wiesmann A, Phillips R L, Mojica M, Pierce L J, Searles A E, Spangrude G J, Lemischka I. Immunity. 2000;12:193–199. - PubMed
-
- Morel F, Galy A, Chen B, Szilvassy S J. Exp Hematol (Charlottesville, Va) 1998;26:440–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

