Recruitment to Golgi membranes of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 is mediated by the cytoplasmic domain of p23
- PMID: 11726511
- PMCID: PMC125325
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6751
Recruitment to Golgi membranes of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 is mediated by the cytoplasmic domain of p23
Abstract
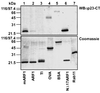
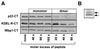
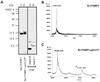
Binding to Golgi membranes of ADP ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) is the first event in the initiation of COPI coat assembly. Based on binding studies, a proteinaceous receptor has been proposed to be critical for this process. We now report that p23, a member of the p24 family of Golgi-resident transmembrane proteins, is involved in ARF1 binding to membranes. Using a cross-link approach based on a photolabile peptide corresponding to the cytoplasmic domain of p23, the GDP form of ARF1 (ARF1-GDP) is shown to interact with p23 whereas ARF1-GTP has no detectable affinity to p23. The p23 binding is shown to localize specifically to a 22 amino acid C-terminal fragment of ARF1. While a monomeric form of a non-photolabile p23 peptide does not significantly inhibit formation of the cross-link product, the corresponding dimeric form does compete efficiently for this interaction. Consistently, the dimeric p23 peptide strongly inhibits ARF1 binding to native Golgi membranes suggesting that an oligomeric form of p23 acts as a receptor for ARF1 before nucleotide exchange takes place.
Figures



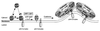
Similar articles
-
Multiple and stepwise interactions between coatomer and ADP-ribosylation factor-1 (Arf1)-GTP.Traffic. 2007 May;8(5):582-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00554.x. Traffic. 2007. PMID: 17451557
-
Correct targeting of plant ARF GTPases relies on distinct protein domains.Traffic. 2008 Jan;9(1):103-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00671.x. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 17988226
-
Dissection of COPI and Arf1 dynamics in vivo and role in Golgi membrane transport.Nature. 2002 May 9;417(6885):187-93. doi: 10.1038/417187a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12000962
-
The COPI system: molecular mechanisms and function.FEBS Lett. 2009 Sep 3;583(17):2701-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.07.032. Epub 2009 Jul 22. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19631211 Review.
-
Membrane curvature and the control of GTP hydrolysis in Arf1 during COPI vesicle formation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Aug;33(Pt 4):619-22. doi: 10.1042/BST0330619. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16042557 Review.
Cited by
-
Localization and regional distribution of p23/TMP21 in the brain.Neurobiol Dis. 2008 Oct;32(1):37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.06.012. Epub 2008 Jul 3. Neurobiol Dis. 2008. PMID: 18652896 Free PMC article.
-
The enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli effector protein NleF binds mammalian Tmp21.Vet Microbiol. 2013 May 31;164(1-2):164-70. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.01.028. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23434013 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of class I and II ADP-ribosylation factors (Arfs) in live cells: GDP-bound class II Arfs associate with the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment independently of GBF1.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Aug;19(8):3488-500. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-04-0373. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18524849 Free PMC article.
-
GTP-binding of ARL-3 is activated by ARL-13 as a GEF and stabilized by UNC-119.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 22;6:24534. doi: 10.1038/srep24534. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27102355 Free PMC article.
-
p23/Tmp21 differentially targets the Rac-GAP beta2-chimaerin and protein kinase C via their C1 domains.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Apr 15;21(8):1398-408. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0735. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20164256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amor J.C., Harrison,D.H., Kahn,R.A. and Ringe,D. (1994) Structure of the human ADP-ribosylation factor 1 complexed with GDP. Nature, 372, 704–708. - PubMed
-
- Antonny B., Beraud-Dufour,S., Chardin,P. and Chabre,M. (1997) N-terminal hydrophobic residues of the G protein ADP ribosylation factor 1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry, 36, 4675–4684. - PubMed
-
- Belden W.J. and Barlowe,C. (1996) Erv25p, a component of COPII-coated vesicles, forms a complex with Emp24p that is required for efficient endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 26939–26949. - PubMed
-
- Beraud-Dufour S., Paris,S., Chabre,M. and Antonny,B. (1999) Dual interaction of ADP ribosylation factor 1 with Sec7 domain and with lipid membranes during catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 37629–37636. - PubMed
-
- Bremser M., Nickel,W., Schweikert,M., Ravazzola,M., Amherdt,M., Hughes,C.A., Söllner,T.H., Rothman,J.E. and Wieland,F.T. (1999) Coupling of coat assembly and vesicle budding to packaging of putative cargo receptors. Cell, 96, 495–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

