CBP/p300 and muscle differentiation: no HAT, no muscle
- PMID: 11726517
- PMCID: PMC125755
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6816
CBP/p300 and muscle differentiation: no HAT, no muscle
Abstract
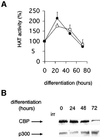
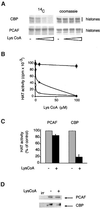
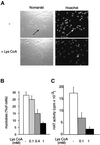
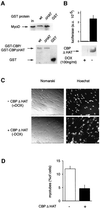
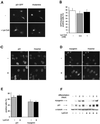
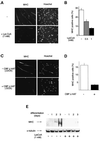
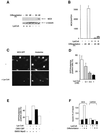
Terminal differentiation of muscle cells follows a precisely orchestrated program of transcriptional regulatory events at the promoters of both muscle-specific and ubiquitous genes. Two distinct families of transcriptional co-activators, GCN5/PCAF and CREB-binding protein (CBP)/p300, are crucial to this process. While both possess histone acetyl-transferase (HAT) activity, previous studies have failed to identify a requirement for CBP/p300 HAT function in myogenic differentiation. We have addressed this issue directly using a chemical inhibitor of CBP/p300 in addition to a negative transdominant mutant. Our results clearly demonstrate that CBP/p300 HAT activity is critical for myogenic terminal differentiation. Furthermore, this requirement is restricted to a subset of events in the differentiation program: cell fusion and specific gene expression. These data help to define the requirements for enzymatic function of distinct coactivators at different stages of the muscle cell differentiation program.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The transcriptional co-activators CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300 play a critical role in cardiac hypertrophy that is dependent on their histone acetyltransferase activity.J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 28;278(9):6838-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211762200. Epub 2002 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12477714
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 interacts with p300, CBP, and PCAF histone acetyltransferases in activation of the LMP1 promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jan 4;97(1):430-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.1.430. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10618435 Free PMC article.
-
The histone acetyltransferase domains of CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300/CBP-associated factor are not necessary for cooperativity with the class II transactivator.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):38715-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106652200. Epub 2001 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11514574
-
CBP and p300: HATs for different occasions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 15;68(6):1145-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.03.045. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15313412 Review.
-
p300/CBP proteins: HATs for transcriptional bridges and scaffolds.J Cell Sci. 2001 Jul;114(Pt 13):2363-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.13.2363. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11559745 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-494-3p inhibits formation of fast oxidative muscle fibres by targeting E1A-binding protein p300 in human-induced pluripotent stem cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1161. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80742-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441918 Free PMC article.
-
An interplay between BRD4 and G9a regulates skeletal myogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 7;10:978931. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.978931. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36158208 Free PMC article.
-
Protein lysine acetylation by p300/CBP.Chem Rev. 2015 Mar 25;115(6):2419-52. doi: 10.1021/cr500452k. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Chem Rev. 2015. PMID: 25594381 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Acetylation regulates the differentiation-specific functions of the retinoblastoma protein.EMBO J. 2004 Apr 7;23(7):1609-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600176. Epub 2004 Mar 25. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15044952 Free PMC article.
-
The small chromatin-binding protein p8 coordinates the association of anti-proliferative and pro-myogenic proteins at the myogenin promoter.J Cell Sci. 2009 Oct 1;122(Pt 19):3481-91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.048678. Epub 2009 Sep 1. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19723804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ait-Si-Ali S. et al. (2000) CBP/p300 histone acetyl-transferase activity is important for the G1/S transition. Oncogene, 19, 2430–2437. - PubMed
-
- Arany Z., Sellers,W.R., Livingston,D.M. and Eckner,R. (1994) E1A-associated p300 and CREB-associated CBP belong to a conserved family of coactivators. Cell, 77, 799–800. - PubMed
-
- Bannister A.J. and Kouzarides,T. (1996) The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature, 384, 641–643. - PubMed
-
- Brownell J.E. and Allis,C.D. (1996) Special HATs for special occasions: linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 6, 176–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

