Spark- and ember-like elementary Ca2+ release events in skinned fibres of adult mammalian skeletal muscle
- PMID: 11731572
- PMCID: PMC2278952
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00379.x
Spark- and ember-like elementary Ca2+ release events in skinned fibres of adult mammalian skeletal muscle
Abstract
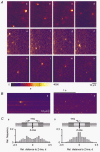
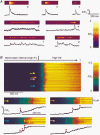
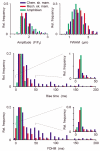
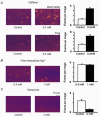
1. Using laser scanning confocal microscopy, we show for the first time elementary Ca2+ release events (ECRE) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in chemically and mechanically skinned fibres from adult mammalian muscle and compare them with ECRE from amphibian skinned fibres. 2. Hundreds of spontaneously occurring events could be measured from individual single skinned mammalian fibres. In addition to spark-like events, we found ember-like events, i.e. long-lasting events of steady amplitude. These two different fundamental release types in mammalian muscle could occur in combination at the same location. 3. The two peaks of the frequency of occurrence for ECRE of mammalian skeletal muscle coincided with the expected locations of the transverse tubular system within the sarcomere, suggesting that ECRE mainly originate at triadic junctions. 4. ECRE in adult mammalian muscle could also be identified at the onset of the global Ca2+ release evoked by membrane depolarisation in mechanically skinned fibres. In addition, the frequency of ECRE was significantly increased by application of 0.5 mM caffeine and reduced by application of 2 mM tetracaine. 5. We conclude that the excitation-contraction coupling process in adult mammalian muscle involves the activation of both spark- and ember-like elementary Ca2+ release events.
Figures
References
-
- Balshaw DM, Xu L, Yamaguchi N, Pasek DA, Meissner G. Calmodulin binding and inhibition of cardiac muscle calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276:20144–20153. - PubMed
-
- Cheng H, Lederer WJ, Cannell MB. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 1993;262:740–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

