Deposition of transthyretin in early stages of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: evidence for toxicity of nonfibrillar aggregates
- PMID: 11733349
- PMCID: PMC1850610
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63050-7
Deposition of transthyretin in early stages of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: evidence for toxicity of nonfibrillar aggregates
Abstract
Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by extracellular deposition of transthyretin (TTR) amyloid fibrils, particularly in the peripheral nervous system. No systematic immunohistochemical data exists relating TTR deposition with FAP progression. We assessed nerves from FAP patients in different stages of disease progression (FAP 0 to FAP 3) for TTR deposition by immunohistochemistry, and for the presence of amyloid fibrils by Congo Red staining. The nature of the deposited material was further studied by electron microscopy. We observed that early in FAP (FAP 0), TTR is already deposited in an aggregated nonfibrillar form, negative by Congo Red staining. This suggested that in vivo, preamyloidogenic forms of TTR exist in the nerve, in a stage before fibril formation. Cytotoxicity of nonfibrillar TTR was assessed in nerves of different FAP stages by immunohistochemistry for macrophage colony-stimulating factor. FAP 0 patients already presented increased axonal expression of macrophage colony-stimulating factor that was maintained in all other stages, in sites related to TTR deposition. Toxicity of synthetic TTR fibrils formed in vitro at physiological pH was studied on a Schwannoma cell line by caspase-3 activation assays and showed that early aggregates but not mature fibrils are toxic to cells. Taken together, these results show that nonfibrillar cytotoxic deposits occur in early stages of FAP.
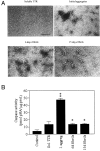
Figures


References
-
- Coimbra A, Andrade C: Familial amyloid polyneuropathy: an electron microscope study of peripheral nerve in five cases. II. Nerve fibril changes. Brain 1971, 94:207-212 - PubMed
-
- Saraiva MJ: Molecular genetics of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 1996, 1:179-188 - PubMed
-
- Coimbra A, Andrade C: Familial amyloid polyneuropathy: an electron microscope study of peripheral nerve in five cases. I. Interstitial changes. Brain 1971, 94:199-206 - PubMed
-
- Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A, Slattery T, Zhao L, Nagashima M, Morser J, Migheli A, Nawroth P, Stern D, Schmidt AM: RAGE and amyloid-beta peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 1996, 382:685-691 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

