Cathepsin B knockout mice are resistant to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury: implications for therapeutic applications
- PMID: 11733355
- PMCID: PMC1850591
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63056-8
Cathepsin B knockout mice are resistant to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury: implications for therapeutic applications
Abstract
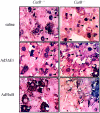
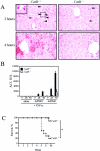
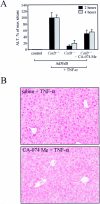
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) contributes to liver injury by inducing hepatocyte apoptosis. Recent evidence suggests that cathepsin B (cat B) contributes to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in vitro. The aim of the present study was to determine whether cat B contributes to TNF-alpha-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury in vivo. Cat B knockout (catB(-/-)) and wild-type (catB(+/+)) mice were first infected with the adenovirus Ad5I kappa B expressing the I kappa B superrepressor to inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B-induced survival signals and then treated with murine recombinant TNF-alpha. Massive hepatocyte apoptosis with mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and activation of caspases 9 and 3 was detected in catB(+/+) mice 2 hours after the injection of TNF-alpha. In contrast, significantly less hepatocyte apoptosis and no detectable release of cytochrome c or caspase activation occurred in the livers of catB(-/-) mice. By 4 hours after TNF-alpha injection, only 20% of the catB(+/+) mice were alive as compared to 85% of catB(-/-) mice. Pharmacological inhibition of cat B in catB(+/+) mice with L-3-trans-(propylcarbamoyl)oxirane-2-carbonyl-L-isoleucyl-L-proline (CA-074 Me) also reduced TNF-alpha-induced liver damage. The present data demonstrate that a cat B-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway plays a pivotal role in TNF-alpha-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury.
Figures


References
-
- Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP: Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol 1999, 17:331-367 - PubMed
-
- Bradham CA, Plumpe J, Manns MP, Brenner DA, Trautwein C: Mechanisms of hepatic toxicity. I. TNF-induced liver injury. Am J Physiol 1998, 275:G387-G392 - PubMed
-
- McClain CJ, Cohen DA: Increased tumor necrosis factor production by monocytes in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 1989, 9:349-351 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

