Identification of receptor-binding sites of monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer
- PMID: 11733378
- PMCID: PMC1850605
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63079-9
Identification of receptor-binding sites of monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer
Abstract
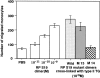
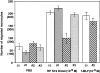
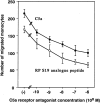
The S19 ribosomal protein (RP S19) cross-linked homo-dimer attracts monocyte migration by binding to C5a receptor on monocytes (H Nishiura, Y Shibuya, T Yamamoto, Laboratory Investigation, 1998, 78:1615-1623). Using site-directed mutants of recombinant RP S19 and synthetic peptides mimicking RP S19 molecular regions, we currently identified the binding sites of the RP S19 dimer to the C5a receptor. The RP S19 dimer activated the receptor by a two-step binding mechanism as in the case of C5a. The first binding site was a basic cluster region containing a -Lys41-His42-Lys43- sequence. The second one was the -Leu131-Asp132-Arg133- moiety, localized 12 residues upstream from the COOH-terminal. The second binding triggered the chemotactic response. The first binding would have a role in achieving a high-binding affinity between the ligand and receptor. The first and second ligand-binding sites of C5a receptor seem to be shared by C5a and the RP S19 dimer, although overall homology between the amino acid sequences of these ligands is only 4%.
Figures







References
-
- Nishiura H, Shibuya Y, Matsubara S, Tanase S, Kambara T, Yamamoto T: Monocyte chemotactic factor in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue: probably a cross-linked derivative of S19 ribosomal protein. J Biol Chem 1996, 271:878-882 - PubMed
-
- Nishiura H, Tanase S, Shibuya Y, Nishimura T, Yamamoto T: Determination of the cross-linked residues in homo-dimerization of S19 ribosomal protein concomitant with exhibition of monocyte chemotactic activity. Lab Invest 1999, 79:915-923 - PubMed
-
- Nishimura T, Horino K, Nishiura H, Shibuya Y, Hiraoka T, Tanase S, Yamamoto T: Apoptotic cells of an epithelial cell line, AsPC-1, release monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer. J Biochem 2001, 129:445-454 - PubMed
-
- Horino K, Nishiura H, Ohsako T, Shibuya Y, Hiraoka T, Kitamura N, Yamamoto T: A monocyte chemotactic factor, S19 ribosomal protein dimer, in phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells. Lab Invest 1998, 78:603-617 - PubMed
-
- Nishiura H, Shibuya Y, Yamamoto T: S19 ribosomal protein cross-linked dimer causes monocyte-predominant infiltration by means of molecular mimicry to complement C5a. Lab Invest 1998, 78:1615-1623 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

