Embryonic gut anomalies in a mouse model of retinoic Acid-induced caudal regression syndrome: delayed gut looping, rudimentary cecum, and anorectal anomalies
- PMID: 11733381
- PMCID: PMC1850584
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63082-9
Embryonic gut anomalies in a mouse model of retinoic Acid-induced caudal regression syndrome: delayed gut looping, rudimentary cecum, and anorectal anomalies
Abstract
Vitamin A and its derivatives such as retinoic acid (RA) are important signaling molecules for morphogenesis of vertebrate embryos. Little is known, however, about morphogenetic factors controlling the development of the gastrointestinal tract and RA is likely to be involved. In the mouse, teratogenic doses of RA cause truncation of the embryonic caudal body axis that parallel the caudal regression syndrome as described in humans. These changes are often associated with anomalies of the lower digestive tract. Overlapping spatiotemporal expression of retinoic acid receptor-beta (RAR beta) and cellular retinol-binding protein I, CRBPI, with Hoxb5 and c-ret in the gut mesoderm imply possible cooperation required for proper neuromuscular development. To determine susceptibility and responsiveness of the developing gut and its neuromusculature to exogenous retinoids we used a mouse model of RA-induced caudal regression syndrome. The results showed that stage-specific RA treatment both in vivo and in vitro affected gut looping/rotation morphogenesis and growth of asymmetrical structures such as the cecum together with delayed differentiation of the gut mesoderm and colonization of the postcecal gut by neural crest-derived enteric neuronal precursors. These observations demonstrate that RA has a direct effect on gut morphogenesis and innervation.
Figures
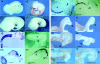
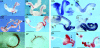
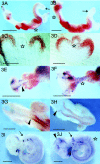
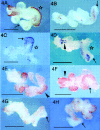
References
-
- Fujimoto T, Hata J, Yokoyma S, Mitomi T: A study of the extracellular matrix protein as the migration pathway of neural crest cell migration in the gut: analysis in human embryos with special reference to the pathogenesis of Hirshsprungs disease. J Pediatr Surg 1989, 24:550-556 - PubMed
-
- Le Douarin NM, Teillet MA: The migration of neural crest cells to the wall of the digestive tract in avian embryo. J Embryonal Exp Morphol 1973, 30:31-48 - PubMed
-
- Gershon MD, Tennyson VM: Microenvironmental factors in the normal and abnormal development of the enteric nervous system. Prog Clin Biol Res 1991, 373:257-276 - PubMed
-
- Gudas LJ: Retinoids and vertebrate development. J Biol Chem 1994, 269:15399-15402 - PubMed
-
- Kessel M, Gruss P: Homeotic transformation of murine vertebrae and concomitant alteration of Hox codes induced by retinoic acid. Cell 1991, 67:89-104 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

