Plasma malondialdehyde and nitric oxide levels in age related macular degeneration
- PMID: 11734513
- PMCID: PMC1723807
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.85.12.1426
Plasma malondialdehyde and nitric oxide levels in age related macular degeneration
Abstract
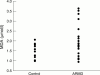
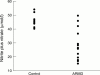
Aims: To evaluate alteration of plasma malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO) levels in patients with exudative age related macular degeneration (ARMD).
Methods: Plasma nitrite plus nitrate concentrations as an index of plasma NO levels and plasma MDA level as a marker of lipid peroxidation were measured in patients with exudative ARMD and age and sex matched healthy subjects.
Results: Significantly higher MDA and lower NO levels were detected in plasma of patients with ARMD compared with their controls (p=0.01, p=0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: The results may support involvement of oxidative damage and vascular theory in the pathogenesis of ARMD as part of the ageing process.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical