The LIM domain gene LMO4 inhibits differentiation of mammary epithelial cells in vitro and is overexpressed in breast cancer
- PMID: 11734645
- PMCID: PMC64702
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.251547698
The LIM domain gene LMO4 inhibits differentiation of mammary epithelial cells in vitro and is overexpressed in breast cancer
Abstract
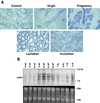
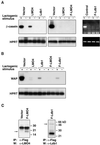
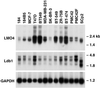
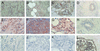
LMO4 belongs to a family of LIM-only transcriptional regulators, the first two members of which are oncoproteins in acute T cell leukemia. We have explored a role for LMO4, initially described as a human breast tumor autoantigen, in developing mammary epithelium and breast oncogenesis. Lmo4 was expressed predominantly in the lobuloalveoli of the mammary gland during pregnancy. Consistent with a role in proliferation, forced expression of this gene inhibited differentiation of mammary epithelial cells. Overexpression of LMO4 mRNA was observed in 5 of 10 human breast cancer cell lines. Moreover, in situ hybridization analysis of 177 primary invasive breast carcinomas revealed overexpression of LMO4 in 56% of specimens. Immunohistochemistry confirmed overexpression in a high percentage (62%) of tumors. These studies imply a role for LMO4 in maintaining proliferation of mammary epithelium and suggest that deregulation of this gene may contribute to breast tumorigenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of LMO4 induces mammary hyperplasia, promotes cell invasion, and is a predictor of poor outcome in breast cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 24;102(21):7659-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502990102. Epub 2005 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15897450 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of an engrailed-LMO4 fusion protein in mammary epithelial cells inhibits mammary gland development in mice.Oncogene. 2004 Feb 26;23(8):1507-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207288. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 14676840
-
Loss of the LIM domain protein Lmo4 in the mammary gland during pregnancy impedes lobuloalveolar development.Oncogene. 2005 Jul 14;24(30):4820-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208638. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15856027
-
[Involvement of LMO4 in tumorigenesis associated epithelial-mesenchymal transition].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011 Jan;40(1):107-11. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2011.01.019. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011. PMID: 21319383 Review. Chinese.
-
Regulation of mammary epithelial cell phenotypes by the helix-loop-helix protein, Id-1.Endocr Relat Cancer. 1999 Mar;6(1):49-50. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0060049. Endocr Relat Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10732787 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles of circular RNAs in regulating the hallmarks of thyroid cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Apr;31(4):507-516. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00736-0. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38316961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The determination of changes in the expression of genes for selected specific transcriptional factors in in vitro ductal breast cancer cells under the influence of paclitaxel.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011 Dec;16(4):610-24. doi: 10.2478/s11658-011-0026-8. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21909792 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila LIM-only is a positive regulator of transcription during thoracic bristle development.Genetics. 2008 Aug;179(4):1989-99. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.090076. Epub 2008 Aug 9. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18689881 Free PMC article.
-
LIM-domain-only proteins in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Feb;13(2):111-22. doi: 10.1038/nrc3418. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23303138 Review.
-
LDB1 overexpression is a negative prognostic factor in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):84258-84270. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12481. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713177 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

