Wnt signaling in breast cancer: have we come full circle?
- PMID: 11737884
- PMCID: PMC138699
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr321
Wnt signaling in breast cancer: have we come full circle?
Abstract
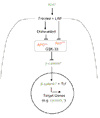
Since the original identification of Wnt1 as a mammary oncogene in mouse mammary tumor virus infected mice, questions have been asked about its relevance to human breast cancer. Wnt1 is now known to be one of a large family of Wnt genes encoding structurally similar secreted signaling proteins, several of which are functionally redundant. The principal intracellular signaling pathway activated by these proteins has been elucidated in recent years. Components of this pathway include proto-oncogene products, such as beta-catenin, and tumor suppressor proteins such as APC. Although WNT1 itself has not been implicated in human breast neoplasms, it has been reported that other WNT genes are sometimes overexpressed in human breast cancer and there is growing evidence that downstream components of the Wnt signaling pathway are activated in a significant proportion of breast tumors.
Figures
References
-
- Nusse R, Varmus HE. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982;31:99–109. - PubMed
-
- Bittner JJ. The milk influence of breast tumors in mice. Science. 1942;95:463. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R, Varmus HE. Wnt genes. Cell. 1992;69:1073–1087. - PubMed
-
- Tsukamoto AS, Grosschedl R, Guzman RC, Parslow T, Varmus HE. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell. 1988;55:619–625. - PubMed
-
- De Ome KB, Faulkin LJ, Bern HA. Development of mammary tumors from hyperplastic alveolar nodules transplanted into gland-free mammary fat pads of female C3H mice. Cancer Res. 1959;19:515–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

