Pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD
- PMID: 11737906
- PMCID: PMC137368
- DOI: 10.1186/cc1049
Pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD
Abstract
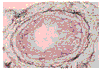
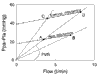
Pulmonary hypertension is a common complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The increase in pulmonary artery pressures is often mild to moderate, but some patients may suffer from severe pulmonary hypertension, and present with a progressively downhill clinical course because of right-sided heart failure added to ventilatory handicap. The cause of pulmonary hypertension in COPD is generally assumed to be hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction leading to permanent medial hypertrophy. However, recent pathological studies point, rather, to extensive remodeling of the pulmonary arterial walls, with prominent intimal changes. These aspects account for minimal reversibility with supplemental oxygen. There may be a case for pharmacological treatment of pulmonary hypertension in selected patients with advanced COPD and right-sided heart failure. Candidate drugs include prostacyclin derivatives, endothelin antagonists and inhaled nitric oxide, all of which have been reported of clinical benefit in primary pulmonary hypertension. However, it will be a challenge for randomized controlled trials to overcome the difficulties of the diagnosis of right ventricular failure and the definition of a relevant primary endpoint in pulmonary hypertensive COPD patients.
Figures
Comment on
-
Acute hemodynamic effects of inhaled nitric oxide, dobutamine and a combination of the two in patients with mild to moderate secondary pulmonary hypertension.Crit Care. 2001 Dec;5(6):355-61. doi: 10.1186/cc1069. Epub 2001 Oct 9. Crit Care. 2001. PMID: 11737925 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Vizza CD, Della Rocca G, Di Roma A, Iacobini C, Pierconti F, Venuta F, Rendina E, Schmid G, Pietropaoli P, Fedele F. Acute hemodynamic effects of inhaled nitric oxide, dobutamine, and their combination in patients with mild to moderate secondary pulmonary hypertension. Crit Care. 2002. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson M, Langhorn CA, Heath D, Barer GR, Howard P. A pathophysiological study of 10 cases of hypoxic cor pulmonale. Q J Med. 1988;66:65–85. - PubMed
-
- Peinado VI, Barbera JA, Abate P, Ramirez J, Roca J, Santos S, Rodriguez-Roisin R. Inflammatory reaction in pulmonary muscular arteries of patients with mild chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;59:1605–1611. - PubMed
-
- Heath D, Williams DR. Pulmonary hypertension. In High-Altitude Medicine and Pathology London: Butterworths, 1989. pp. 102–114.
-
- Lejeune P, Mols P, Naeije R, Hallemans R, Mélot C. Acute hemodynamic effects of controlled oxygen therapy in decompensated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Crit Care Med. 1984;12:1032–1035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

