Novel function of the cyclin A binding site of E2F in regulating p53-induced apoptosis in response to DNA damage
- PMID: 11739724
- PMCID: PMC134205
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.78-93.2002
Novel function of the cyclin A binding site of E2F in regulating p53-induced apoptosis in response to DNA damage
Abstract
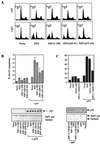
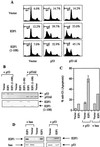
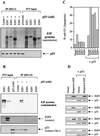
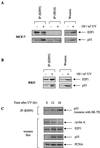
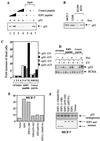
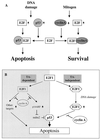
We demonstrate here that the E2F1 induced by DNA damage can bind to and promote the apoptotic function of p53 via the cyclin A binding site of E2F1. This function of E2F1 does not require its DP-1 binding, DNA binding, or transcriptional activity and is independent of mdm2. All the cyclin A binding E2F family members can interact and cooperate with p53 to induce apoptosis. This suggests a novel role for E2F in regulating apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Cyclin A, but not cyclin E, prevents E2F1 from interacting and cooperating with p53 to induce apoptosis. However, in response to DNA damage, cyclin A levels decrease, with a concomitant increase in E2F1-p53 complex formation. These results suggest that the binding of E2F1 to p53 can specifically stimulate the apoptotic function of p53 in response to DNA damage.
Figures



Similar articles
-
E2F1 induces phosphorylation of p53 that is coincident with p53 accumulation and apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;22(15):5308-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5308-5318.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12101227 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the E2F-1/p53/Bax pathway by tauroursodeoxycholic acid in amyloid beta-peptide-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells.J Neurochem. 2004 Aug;90(3):567-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02517.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15255934
-
E2F1-induced apoptosis requires DNA binding but not transactivation and is inhibited by the retinoblastoma protein through direct interaction.Genes Dev. 1997 Jul 15;11(14):1840-52. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.14.1840. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9242491
-
The role of the transcription factor DP in apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2003 Oct;8(5):461-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1025586207239. Apoptosis. 2003. PMID: 12975577 Review.
-
E2F1 pathways to apoptosis.FEBS Lett. 2002 Oct 2;529(1):122-5. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03270-2. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12354623 Review.
Cited by
-
Survivin: A molecular biomarker in cancer.Indian J Med Res. 2015 Apr;141(4):389-97. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.159250. Indian J Med Res. 2015. PMID: 26112839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DLGAP5 triggers proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer by stabilizing E2F1 via USP11.Oncogene. 2024 Feb;43(8):594-607. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02932-y. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38182895
-
Opposing roles of E2Fs in cell proliferation and death.Cancer Biol Ther. 2004 Dec;3(12):1208-11. doi: 10.4161/cbt.3.12.1494. Epub 2004 Dec 21. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15662116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of cyclins, p53, and Ki-67 in cervical squamous cell carcinomas: overexpression of cyclin A is a poor prognostic factor in stage Ib and II disease.Virchows Arch. 2005 Jun;446(6):626-33. doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-1252-0. Epub 2005 May 13. Virchows Arch. 2005. PMID: 15891905
-
Cdh1 regulates cell cycle through modulating the claspin/Chk1 and the Rb/E2F1 pathways.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jul;20(14):3305-16. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-01-0092. Epub 2009 May 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19477924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates, S., A. Phillips, P. Clark, F. Stott, G. Peters, R. Ludwig, and K. Vousden. 1998. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 395:124–125. - PubMed
-
- Clarke, A. R., C. A. Purdie, D. J. Harrison, R. G. Morris, C. C. Bird, M. L. Hooper, and A. H. Wyllie. 1993. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature 362:849–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
