Na,K-ATPase activity is required for formation of tight junctions, desmosomes, and induction of polarity in epithelial cells
- PMID: 11739775
- PMCID: PMC60750
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.12.3717
Na,K-ATPase activity is required for formation of tight junctions, desmosomes, and induction of polarity in epithelial cells
Abstract
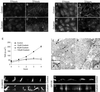
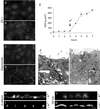
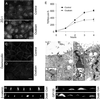
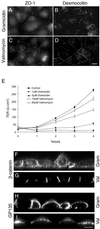
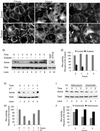
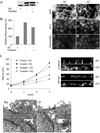
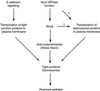
Na,K-ATPase is a key enzyme that regulates a variety of transport functions in epithelial cells. In this study, we demonstrate a role for Na,K-ATPase in the formation of tight junctions, desmosomes, and epithelial polarity with the use of the calcium switch model in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Inhibition of Na,K-ATPase either by ouabain or potassium depletion prevented the formation of tight junctions and desmosomes and the cells remained nonpolarized. The formation of bundled stress fibers that appeared transiently in control cells was largely inhibited in ouabain-treated or potassium-depleted cells. Failure to form stress fibers correlated with a large reduction of RhoA GTPase activity in Na,K-ATPase-inhibited cells. In cells overexpressing wild-type RhoA GTPase, Na,K-ATPase inhibition did not affect the formation of stress fibers, tight junctions, or desmosomes, and epithelial polarity developed normally, suggesting that RhoA GTPase is an essential component downstream of Na,K-ATPase-mediated regulation of these junctions. The effects of Na,K-ATPase inhibition were mimicked by treatment with the sodium ionophore gramicidin and were correlated with the increased intracellular sodium levels. Furthermore, ouabain treatment under sodium-free condition did not affect the formation of junctions and epithelial polarity, suggesting that the intracellular Na(+) homeostasis plays a crucial role in generation of the polarized phenotype of epithelial cells. These results thus demonstrate that the Na,K-ATPase activity plays an important role in regulating both the structure and function of polarized epithelial cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Na-K-ATPase in the assembly of tight junctions.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Sep;285(3):F388-96. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00439.2002. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12890662
-
Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit is required for epithelial polarization, suppression of invasion, and cell motility.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Feb;12(2):279-95. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.2.279. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11179415 Free PMC article.
-
Na,K-ATPase inhibition alters tight junction structure and permeability in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003 Jun;284(6):C1497-507. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00355.2002. Epub 2003 Feb 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12570983
-
Na,K-ATPase and epithelial tight junctions.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(6):2130-48. doi: 10.2741/3367. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273189 Review.
-
Multiple functions of Na,K-ATPase in epithelial cells.Semin Nephrol. 2005 Sep;25(5):328-34. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2005.03.008. Semin Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 16139688 Review.
Cited by
-
Na,K-ATPase is a target of cigarette smoke and reduced expression predicts poor patient outcome of smokers with lung cancer.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):L1150-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00384.2010. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22345575 Free PMC article.
-
T cell activation causes diarrhea by increasing intestinal permeability and inhibiting epithelial Na+/K+-ATPase.J Clin Invest. 2002 Dec;110(11):1739-47. doi: 10.1172/JCI15695. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12464679 Free PMC article.
-
Na+/K+-ATPase α1 identified as an abundant protein in the blood-labyrinth barrier that plays an essential role in the barrier integrity.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 31;6(1):e16547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016547. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21304972 Free PMC article.
-
Na+/K+-ATPase: More than an Electrogenic Pump.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 1;25(11):6122. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116122. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alveolar epithelium and Na,K-ATPase in acute lung injury.Intensive Care Med. 2007 Jul;33(7):1243-1251. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0661-8. Epub 2007 May 25. Intensive Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17530222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, Gonzalez S, Cereijido M, Matter K. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1996;134:1031–1049. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Contreras RG, Shoshani L, Flores-Maldonado C, Lazaro A, Cereijido M. Relationship between Na+,K+-ATPase and cell attachment. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:4223–4232. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez R, Malnic G. H+ ATPase and Cl− interaction in regulation of MDCK cell pH. J Membr Biol. 1998;163:137–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

