A genomewide search for type 2 diabetes-susceptibility genes in indigenous Australians
- PMID: 11742441
- PMCID: PMC384914
- DOI: 10.1086/338626
A genomewide search for type 2 diabetes-susceptibility genes in indigenous Australians
Abstract
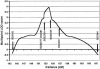
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes among Australian residents is 7.5%; however, prevalence rates up to six times higher have been reported for indigenous Australian communities. Epidemiological evidence implicates genetic factors in the susceptibility of indigenous Australians to type 2 diabetes and supports the hypothesis of the "thrifty genotype," but, to date, the nature of the genetic predisposition is unknown. We have ascertained clinical details from a community of indigenous Australian descent in North Stradbroke Island, Queensland. In this population, the phenotype is characterized by severe insulin resistance. We have conducted a genomewide scan, at an average resolution of 10 cM, for type 2 diabetes-susceptibility genes in a large multigeneration pedigree from this community. Parametric linkage analysis undertaken using FASTLINK version 4.1p yielded a maximum two-point LOD score of +2.97 at marker D2S2345. Multipoint analysis yielded a peak LOD score of +3.9 <1 cM from marker D2S2345, with an 18-cM 3-LOD support interval. Secondary peak LOD scores were noted on chromosome 3 (+1.8 at recombination fraction [theta] 0.05, at marker D3S1311) and chromosome 8 (+1.77 at theta=0.0, at marker D8S549). These chromosomal regions are likely to harbor novel susceptibility genes for type 2 diabetes in the indigenous Australian population.
Figures


References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Genethon, http://www.genethon.fr/ (for marker locations)
-
- Genetic Location Database, The, http://cedar.genetics.soton.ac.uk/public_html/ldb.html (for marker and chromosome locations)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for type 2 diabetes [MIM 125853], NIDDM1 [MIM 601283], NIDDM2 [MIM 601467], CAPN10 [MIM 605286], Grb14 [MIM 601524], glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 [MIM 138430], KCNJ3 [MIM 601534], and type 1 protein phosphatase inhibitor 2 [MIM 601792])
References
-
- Alessi DR, Street AJ, Cohen P, Cohen PT (1993) Inhibitor-2 functions like a chaperone to fold three expressed isoforms of mammalian protein phosphatase-1 into a conformation with the specificity and regulatory properties of the native enzyme. Eur J Biochem 213:1055–1066 - PubMed
-
- Bastian P (1979) Coronary heart disease in tribal Aborigines—the West Kimberley survey. Aust N Z J Med 9:284–292 - PubMed
-
- Bell GI, Pilkis SJ, Weber IT, Polonsky KS (1996) Glucokinase mutations, insulin secretion, and diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Physiol 58:171–186 - PubMed
-
- Bowden DW, Sale M, Howard TD, Qadri A, Spray BJ, Rothschild CB, Akots G, Rich SS, Freedman BI (1997) Linkage of genetic markers on human chromosomes 20 and 12 to NIDDM in Caucasian sib pairs with a history of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 46:882–886 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

