The structure of bovine IF(1), the regulatory subunit of mitochondrial F-ATPase
- PMID: 11742976
- PMCID: PMC125800
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.24.6990
The structure of bovine IF(1), the regulatory subunit of mitochondrial F-ATPase
Abstract
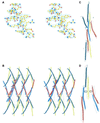
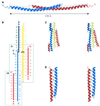
In mitochondria, the hydrolytic activity of ATP synthase is regulated by an inhibitor protein, IF(1). Its binding to ATP synthase depends on pH, and below neutrality, IF(1) is dimeric and forms a stable complex with the enzyme. At higher pH values, IF(1) forms tetramers and is inactive. In the 2.2 A structure of the bovine IF(1) described here, the four monomers in the asymmetric unit are arranged as a dimer of dimers. Monomers form dimers via an antiparallel alpha-helical coiled coil in the C-terminal region. Dimers are associated into oligomers and form long fibres in the crystal lattice, via coiled-coil interactions in the N-terminal and inhibitory regions (residues 14-47). Therefore, tetramer formation masks the inhibitory region, preventing IF(1) binding to ATP synthase.
Figures

References
-
- Abrahams J.P. and Leslie,A.G.W. (1996) Methods used in the structure determination of bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase. Acta Crystallogr. D, 52, 30–42. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T. et al. (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D, 54, 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Cabezón E., Butler,P.J.G., Runswick,M.J. and Walker,J.E. (2000a) Modulation of the oligomerization state of bovine F1-ATPase inhibitor protein, IF1, by pH. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 25460–25464. - PubMed
-
- Cabezón E., Arechaga,I., Butler,P.J.G. and Walker,J.E. (2000b) Dimerization of bovine F1-ATPase by binding the inhibitor protein, IF1. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 28353–28355. - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D, 50, 760–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

