Structure of a two-domain fragment of HIV-1 integrase: implications for domain organization in the intact protein
- PMID: 11743009
- PMCID: PMC125787
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.24.7333
Structure of a two-domain fragment of HIV-1 integrase: implications for domain organization in the intact protein
Abstract
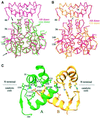
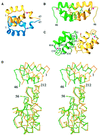
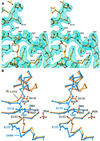
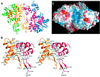
Retroviral integrase, an essential enzyme for replication of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) and other retroviruses, contains three structurally distinct domains, an N-terminal domain, the catalytic core and a C-terminal domain. To elucidate their spatial arrangement, we have solved the structure of a fragment of HIV-1 integrase comprising the N-terminal and catalytic core domains. This structure reveals a dimer interface between the N-terminal domains different from that observed for the isolated domain. It also complements the previously determined structure of the C-terminal two domains of HIV-1 integrase; superposition of the conserved catalytic core of the two structures results in a plausible full-length integrase dimer. Furthermore, an integrase tetramer formed by crystal lattice contacts bears structural resemblance to a related bacterial transposase, Tn5, and exhibits positively charged channels suitable for DNA binding.
Figures
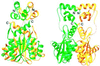
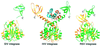

References
-
- Aldaz H., Schuster,E. and Baker,T.A. (1996) The interwoven architecture of the Mu transposase couples DNA synapsis to catalysis. Cell, 85, 257–269. - PubMed
-
- Asante-Appiah E. and Skalka,A.M. (1997) Molecular mechanisms in retrovirus DNA integration. Antiviral Res., 36, 139–156. - PubMed
-
- Brown P.O. (1997) Integration. In Coffin,J.M., Hughes,S.H. and Varmus,H.E. (eds), Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 161–203.
-
- Brünger A.T. et al. (1998) Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D, 54, 905–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

