Phosphorylation of Ser(982) in the sodium bicarbonate cotransporter kNBC1 shifts the HCO(3)(-) : Na(+) stoichiometry from 3 : 1 to 2 : 1 in murine proximal tubule cells
- PMID: 11744745
- PMCID: PMC2278987
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00659.x
Phosphorylation of Ser(982) in the sodium bicarbonate cotransporter kNBC1 shifts the HCO(3)(-) : Na(+) stoichiometry from 3 : 1 to 2 : 1 in murine proximal tubule cells
Erratum in
- J Physiol 2002 Feb 1;538(Pt 3):1003
Abstract
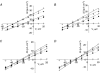
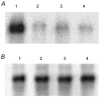
1. Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) modulates proximal tubule sodium and bicarbonate absorption by decreasing the rate of apical Na(+)-H(+) exchange and basolateral sodium bicarbonate efflux, through activation of protein kinase A (PKA). The electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter kNBC1 mediates basolateral sodium and bicarbonate efflux in the proximal tubule by coupling the transport of 1 Na(+) cation to that of 3 HCO(3)(-) anions. In this work we studied the effects of cAMP on the function of kNBC1 expressed heterologously in a proximal tubule cell line. 2. A mouse renal proximal tubule cell line, deficient in electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransport function, was transfected with kNBC1. Cells were grown on a permeable support to confluence, mounted in an Ussing chamber and permeabilized apically with amphotericin B. Current through the cotransporter was isolated as the difference current due to the reversible inhibitor dinitrostilbene disulfonate. The HCO(3)(-) : Na(+) stoichiometry of kNBC1 was calculated from its reversal potential by measuring the current-voltage relationships of the cotransporter at different Na(+) concentration gradients. 3. Addition of the potent cAMP agonist 8-Br-cAMP caused the stoichiometry of kNBC1 to shift from 3 HCO(3)(-) : 1 Na(+) to 2 HCO(3)(-) : 1 Na(+). Pretreatment of the cells with the PKA inhibitor H-89 abolished the effect of the agonist on the stoichiometry change. Replacing Ser(982) at the C-terminus consensus PKA phosphorylation site with alanine resulted in a failure of PKA to phosphorylate the transporter and induce a stoichiometry shift. 4. Our data indicate that cAMP modulates the stoichiometry of kNBC1 through activation of PKA. The change in stoichiometry from 3 : 1 to 2 : 1 is predicted to cause a shift in the direction of basolateral membrane sodium bicarbonate transport from efflux to influx. Ser(982) in the C-terminus of kNBC1 is a target for PKA phosphorylation. This is the first example of modulation of the stoichiometry of a membrane transporter by phosphorylation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation-induced modulation of pNBC1 function: distinct roles for the amino- and carboxy-termini.J Physiol. 2003 Jun 15;549(Pt 3):673-82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.042226. Epub 2003 May 2. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12730338 Free PMC article.
-
The stoichiometry of the electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter NBC1 is cell-type dependent.J Physiol. 2001 Mar 15;531(Pt 3):597-603. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0597h.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11251043 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the sodium bicarbonate cotransporter kNBC1 function: role of Asp(986), Asp(988) and kNBC1-carbonic anhydrase II binding.J Physiol. 2002 Nov 1;544(3):679-85. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.029777. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12411514 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants and significance of regulation of electrogenic Na(+)-HCO(3)(-) cotransporter stoichiometry.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002 Nov;283(5):F876-87. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00148.2002. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12372762 Review.
-
Na+:HCO(3-) cotransporters (NBC): cloning and characterization.J Membr Biol. 2001 Sep 15;183(2):71-84. doi: 10.1007/s00232-001-0055-8. J Membr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11562789 Review.
Cited by
-
PIP2 hydrolysis stimulates the electrogenic Na+-bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1-B and -C variants expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes.J Physiol. 2012 Dec 1;590(23):5993-6011. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.242479. Epub 2012 Sep 10. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22966160 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic duct secretion: experimental methods, ion transport mechanisms and regulation.J Physiol Biochem. 2008 Sep;64(3):243-57. doi: 10.1007/BF03178846. J Physiol Biochem. 2008. PMID: 19244938 Review.
-
Transport Metabolons and Acid/Base Balance in Tumor Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 7;12(4):899. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040899. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32272695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical amino acid residues involved in the electrogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter kNBC1-mediated transport.J Physiol. 2005 Jun 15;565(Pt 3):717-30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.084988. Epub 2005 Apr 7. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15817634 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-induced modulation of pNBC1 function: distinct roles for the amino- and carboxy-termini.J Physiol. 2003 Jun 15;549(Pt 3):673-82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.042226. Epub 2003 May 2. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12730338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abuladze N, Lee I, Newman D, Hwang J, Boorer K, Pushkin A, Kurtz I. Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and functional expression of the human pancreatic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1998a;273:17689–17695. - PubMed
-
- Abuladze N, Lee I, Newman D, Hwang J, Pushkin A, Kurtz I. Axial heterogeneity of sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter expression in the rabbit proximal tubule. American Journal of Physiology. 1998b;274:F628–633. - PubMed
-
- Abuladze N, Song M, Pushkin A, Newman D, Lee I, Nicholas S, Kurtz I. Structural organization of the human NBC1 gene: kNBC1 is transcribed from an alternative promoter in intron 3. Gene. 2000;251:109–122. - PubMed
-
- Alpern R, Rector RC., Jr . Renal acidification mechanisms. In: Brenner BM, Rector FC, editors. The Kidney. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders; 1996. pp. 408–471.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

