Induction of gamma interferon and nitric oxide by truncated pneumolysin that lacks pore-forming activity
- PMID: 11748170
- PMCID: PMC127632
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.1.107-113.2002
Induction of gamma interferon and nitric oxide by truncated pneumolysin that lacks pore-forming activity
Abstract
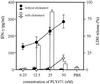
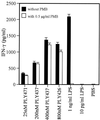
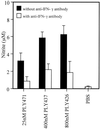
Pneumolysin (PLY), an important virulence factor of Streptococcus pneumoniae, is known to exert various effects on the host immune cells, including cytokine induction, in addition to its known cytolytic activity as a member of the thiol-activated cytolysins. It is of interest to determine whether cytolytic activity is involved in triggering the cytokine production. In this study, we constructed full-length recombinant PLY and noncytolytic truncated PLYs with C-terminal deletions to examine the response of spleen cells to these PLY preparations. When cytolytic activity was blocked by treatment with cholesterol, full-length PLY was capable of inducing gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) production. Truncated PLYs that originally exhibited no cytolytic activity were also active in IFN-gamma induction. Therefore, the IFN-gamma-inducing ability of PLY appeared to be independent of the cytolytic activity. Furthermore, IFN-gamma-inducing preparations were also capable of inducing nitric oxide synthase expression and nitric oxide (NO) production, and the addition of neutralizing antibody to IFN-gamma abolished the NO production. These results clearly demonstrated that PLY is capable of inducing IFN-gamma production in spleen cells by a mechanism different from pore formation and that the induced IFN-gamma stimulates NO production. These findings were discussed with reference to the contribution of PLY to the virulence of S. pneumoniae in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Seeligeriolysin O, a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin of Listeria seeligeri, induces gamma interferon from spleen cells of mice.Infect Immun. 2003 Jan;71(1):234-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.234-241.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12496171 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociated linkage of cytokine-inducing activity and cytotoxicity to different domains of listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes.Infect Immun. 2002 Mar;70(3):1334-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1334-1341.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11854218 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumolysin, a protein toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae, induces nitric oxide production from macrophages.Infect Immun. 1999 Aug;67(8):3750-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.3750-3756.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10417133 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of domain 4 of pneumolysin from Streptococcus pneumoniae in cytolytic activity as determined by truncated proteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Feb 16;281(1):37-44. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4297. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11178957
-
The Yin and Yang of Pneumolysin During Pneumococcal Infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 22;13:878244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.878244. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35529870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Critical involvement of pneumolysin in production of interleukin-1alpha and caspase-1-dependent cytokines in infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae in vitro: a novel function of pneumolysin in caspase-1 activation.Infect Immun. 2008 Apr;76(4):1547-57. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01269-07. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18195026 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumolysin-dependent and -independent gene expression identified by cDNA microarray analysis of THP-1 human mononuclear cells stimulated by Streptococcus pneumoniae.Infect Immun. 2003 Apr;71(4):2087-94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.2087-2094.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12654830 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus pyogenes cytolysin-mediated translocation does not require pore formation by streptolysin O.EMBO Rep. 2010 May;11(5):400-5. doi: 10.1038/embor.2010.37. Epub 2010 Mar 26. EMBO Rep. 2010. PMID: 20339385 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput Measurement of Plasma Membrane Resealing Efficiency in Mammalian Cells.J Vis Exp. 2019 Jan 7;(143):10.3791/58351. doi: 10.3791/58351. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 30663635 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumococcal behavior and host responses during bronchopneumonia are affected differently by the cytolytic and complement-activating activities of pneumolysin.Infect Immun. 2003 Apr;71(4):1813-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.1813-1819.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12654795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, J. E., A. M. Berry, J. C. Paton, J. B. Rubins, P. W. Andrew, and T. J. Mitchell. 1998. Amino acid changes affecting the activity of pneumolysin alter the behaviour of pneumococci in pneumonia. Microb. Pathog. 24: 167–174 - PubMed
-
- Alouf, J. E. 1999. Introduction to the family of the structurally related cholesterol-binding cytolysins (‘sulfhydryl-activated’ toxins), p. 443–456. In J. E. Alouf and J. H. Freer (ed.), The comprehensive sourcebook of bacterial protein toxins, 2nd ed. Academic Press, London, England
-
- Baba, H., I. Kawamura, C. Kohda, T. Nomura, Y. Ito, T. Kimoto, I. Watanabe, S. Ichiyama, and M. Mitsuyama. 2001. Essential role of domain 4 of pneumolysin from Streptococcus pneumoniae in cytolytic activity as determined by truncated proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 281: 37–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

