Deficient humoral responses underlie susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii in CD4-deficient mice
- PMID: 11748181
- PMCID: PMC127596
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.1.185-191.2002
Deficient humoral responses underlie susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii in CD4-deficient mice
Abstract
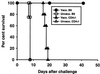
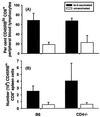
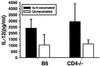
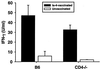
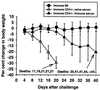
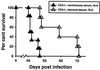
Resistance to infection with Toxoplasma gondii was studied in mice lacking CD4 expression. Such mice developed more brain cysts and survived for a shorter time than did wild-type controls after peroral infection with ME49 cysts. After immunization with the ts-4 strain of T. gondii, CD4-deficient mice exhibited impaired resistance to a challenge infection with virulent RH tachyzoites. Thus, deficient CD4 expression increases the susceptibility of mice to a primary peroral T. gondii infection with cysts and impairs their ability to be successfully vaccinated. CD8(+) T cells from blood or spleens of Toxoplasma-infected, CD4-deficient mice expressed markers of activation at frequencies similar to those of infected wild-type mice. Production of IFN-gamma in vitro was moderately depressed, and levels of Toxoplasma-specific immunoglobulin G2a in serum were substantially lower than in wild-type mice. Administration of Toxoplasma-immune serum to ts-4-vaccinated CD4-deficient mice significantly improved their resistance to RH challenge. Also, the survival of CD4-deficient mice chronically infected with ME49 was significantly prolonged by administration of immune serum. These results demonstrate that in addition to CD8(+) T cells and IFN-gamma, which are known to be critical for resistance, CD4(+) cells also contribute significantly to protection against chronic T. gondii infections and against challenge infections with highly virulent tachyzoites in immunized mice via their role as helper cells for production of isotype-switched antibodies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunity in the spleen and blood of mice immunized with irradiated Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2016 Aug;205(4):297-314. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0447-5. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26732075
-
DNA immunization with eukaryotic initiation factor-2α of Toxoplasma gondii induces protective immunity against acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice.Vaccine. 2013 Dec 16;31(52):6225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.10.034. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 24183979
-
Humoral responses and immune protection in mice immunized with irradiated T. gondii tachyzoites and challenged with three genetically distinct strains of T. gondii.Immunol Lett. 2011 Aug 30;138(2):187-96. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.04.007. Epub 2011 Apr 25. Immunol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21545808
-
The immune system utilizes two distinct effector mechanisms of T cells depending on two different life cycle stages of a single pathogen, Toxoplasma gondii, to control its cerebral infection.Parasitol Int. 2020 Jun;76:102030. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2019.102030. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Parasitol Int. 2020. PMID: 31778800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-gamma- and perforin-mediated immune responses for resistance against Toxoplasma gondii in the brain.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2011 Oct 4;13:e31. doi: 10.1017/S1462399411002018. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 22005272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Toxoplasma gondii infection on the brain.Schizophr Bull. 2007 May;33(3):745-51. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbm008. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Schizophr Bull. 2007. PMID: 17322557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organ- and disease-stage-specific regulation of Toxoplasma gondii-specific CD8-T-cell responses by CD4 T cells.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5790-801. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00098-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988257 Free PMC article.
-
VCAM-1/α4β1 integrin interaction is crucial for prompt recruitment of immune T cells into the brain during the early stage of reactivation of chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii to prevent toxoplasmic encephalitis.Infect Immun. 2014 Jul;82(7):2826-39. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01494-13. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24752515 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-mediated immunity to Toxoplasma gondii develops primarily by local Th1 host immune responses in the absence of parasite replication.J Immunol. 2009 Jan 15;182(2):1069-78. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.2.1069. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19124750 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression with cyclophosphamide favors reinfection with recombinant Toxoplasma gondii strains.Parasite. 2012 Aug;19(3):249-57. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2012193249. Parasite. 2012. PMID: 22910667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araujo, F. G. 1992. Depletion of CD4+ T cells but not inhibition of the protective activity of IFN-gamma prevents cure of toxoplasmosis mediated by drug therapy in mice. J. Immunol. 149: 3003–3007. - PubMed
-
- Buller, R. M. L., K. L. Holmes, A. Hugin, T. N. Fredrickson, and H. C. Morse III. 1987. Induction of cytotoxic T-cell responses in vivo in the absence of CD4 helper cells. Nature 328: 77–79. - PubMed
-
- Denkers, E. Y., G. Yap, T. Scharton-Kersten, H. Charest, B. A. Butcher, P. Caspar, S. Hieny, and A. Sher. 1997. Perforin-mediated cytolysis plays a limited role in host resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 159: 1903–1908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

