Biological characterization of lipopolysaccharide from Treponema pectinovorum
- PMID: 11748185
- PMCID: PMC127642
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.1.211-217.2002
Biological characterization of lipopolysaccharide from Treponema pectinovorum
Abstract
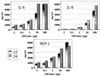
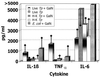
This study investigated the endotoxic and biological properties of purified lipopolysaccharide (LPS) isolated from an oral spirochete, Treponema pectinovorum. Endotoxicity, measured by Limulus amoebocyte lysate kinetic assay, showed that the LPS contained 1.28 endotoxin units per microg of purified LPS, which was approximately 4,000 times less than Escherichia coli O55:B5 LPS. To determine in vivo endotoxicity, LPS responder mice were administered LPS following galactosamine (GalN) sensitization. The LPS induced neither endotoxic symptoms nor lethality for 96 h, suggesting negligible or very low endotoxicity. In contrast, infection with live T. pectinovorum induced 100% lethality within 12 h in GalN-sensitized LPS responder mice, indicating an endotoxin-like property of this treponeme. Heat-killed microorganisms exhibited no lethality in GalN-sensitized mice, suggesting that the endotoxicity was associated with heat-labile components. To determine cytokine and chemokine induction by LPS, human gingival fibroblasts were stimulated and secretion of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, gamma interferon, IL-6, IL-8, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) was assessed. The purified LPS induced significant amounts of only IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1, although they were substantially lower than levels after challenge with live T. pectinovorum. After injection of LPS or live or heat-killed T. pectinovorum, serum was collected from mice and analyzed for proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and IL-6. LPS induced only IL-6 consistently. Both live and heat-killed T. pectinovorum induced serum IL-6, which was higher than the level detected following LPS administration. Importantly, live bacteria elicited systemic TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels similar to those induced by a lethal dose of live E. coli O111. The results indicated that T. pectinovorum LPS has very low or no endotoxicity, although it can elicit low levels of cytokines from host cells. In contrast to the LPS, live T. pectinovorum demonstrated in vivo toxicity, which was associated with serum IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and IL-6, suggesting an endotoxin-like property of a heat-labile molecule(s) of the spirochete.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokine responses to treponema pectinovorum and treponema denticola in human gingival fibroblasts.Infect Immun. 2000 Sep;68(9):5284-92. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.5284-5292.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10948156 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality and tumor necrosis factor synthesis by Rhodobacter sphaeroides diphosphoryl lipid A is dependent on corticosterone induction.Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2581-7. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2581-2587.1992. Infect Immun. 1992. PMID: 1612727 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental modulation of oral treponeme virulence in a murine model.Infect Immun. 1999 Jun;67(6):2783-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.6.2783-2789.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10338481 Free PMC article.
-
A novel synthetic lipid A analog with low endotoxicity, DT-5461, prevents lethal endotoxemia.Infect Immun. 1995 Aug;63(8):2859-66. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.8.2859-2866.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7622206 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of endotoxin shock and endotoxin hypersensitivity.Immunobiology. 1993 Apr;187(3-5):346-56. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80349-9. Immunobiology. 1993. PMID: 8330903 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the cell surface glycolipid from Spirochaeta aurantia.Glycoconj J. 2009 Dec;26(9):1097-108. doi: 10.1007/s10719-009-9230-4. Glycoconj J. 2009. PMID: 19214746
-
Oral Spirochete Treponema denticola Intraoral Infection Reveals Unique miR-133a, miR-486, miR-126-3p, miR-126-5p miRNA Expression Kinetics during Periodontitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12105. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512105. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569480 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and proinflammatory cytokines by the major surface proteins of Treponema maltophilum and Treponema lecithinolyticum, the phylogenetic group IV oral spirochetes associated with periodontitis and endodontic infections.Infect Immun. 2005 Jan;73(1):268-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.268-276.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15618163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beutler, B. I., W. Milsark, and A. Cerami. 1985. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor (TNF) protects mice from the lethal effect of endotoxin. Science 229: 869–871. - PubMed
-
- Birkedal-Hansen, H. 1993. Role of cytokines and inflammatory mediators in tissue destruction. J. Periodontal Res. 28: 500–510. - PubMed
-
- Chow, J. C., D. W. Young, D. T. Golenbock, W. J. Christ, and F. Gusovsky. 1999. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 10689–10692. - PubMed
-
- Dahle, U. R., L. Tronstad, and I. Olsen. 1996. 3-Hydroxy fatty acids in a lipopolysaccharide-like material from Treponema denticola strain FM. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 12: 202–205. - PubMed
-
- Darveau, R. P. 2000. Oral innate host defense responses: interactions with microbial communities and their role in the development of disease, p. 169–218. In H. K. Kuramitsu and R. P. Ellen (ed.), Oral bacterial ecology: the molecular basis. Horizon Scientific Press, Wymondham, United Kingdom.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

