The regulation of T cell homeostasis and autoimmunity by T cell-derived LIGHT
- PMID: 11748260
- PMCID: PMC209470
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI13827
The regulation of T cell homeostasis and autoimmunity by T cell-derived LIGHT
Abstract
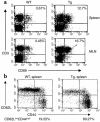
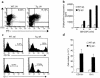
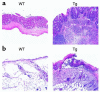
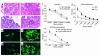
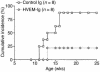
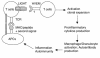
Costimulatory molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) play an important role in T cell activation and expansion. However, little is known about the surface molecules involved in direct T-T cell interaction required for their activation and expansion. LIGHT, a newly discovered TNF superfamily member (TNFSF14), is expressed on activated T cells and immature dendritic cells. Here we demonstrate that blockade of LIGHT activity can reduce anti-CD3-mediated proliferation of purified T cells, suggesting that T cell-T cell interaction is essential for this proliferation. To test the in vivo activity of T cell-derived LIGHT in immune homeostasis and function, transgenic (Tg) mice expressing LIGHT in the T cell lineage were generated. LIGHT Tg mice have a significantly enlarged T cell compartment and a hyperactivated peripheral T cell population. LIGHT Tg mice spontaneously develop severe autoimmune disease manifested by splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, glomerulonephritis, elevated autoantibodies, and severe infiltration of various peripheral tissues. Furthermore, the blockade of LIGHT activity ameliorates the severity of T cell-mediated diseases. Collectively, these findings establish a crucial role for this T cell-derived costimulatory ligand in T cell activation and expansion; moreover, the dysregulation of T cell-derived LIGHT leads to altered T cell homeostasis and autoimmune disease.
Figures


Comment in
-
Turning on LIGHT.J Clin Invest. 2001 Dec;108(12):1741-2. doi: 10.1172/JCI14651. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11748255 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fu YX, Chaplin DD. Development and maturation of secondary lymphoid tissues. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:399–433. - PubMed
-
- Ware CF, VanArsdale TL, Crowe PD, Browning JL. The ligands and receptors of the lymphotoxin system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;198:175–218. - PubMed
-
- Sedgwick JD, Riminton DS, Cyster JG, Korner H. Tumor necrosis factor: a master-regulator of leukocyte movement. Immunol Today. 2000;21:110–113. - PubMed
-
- Ruddle NH. Lymphoid neo-organogenesis: lymphotoxin’s role in inflammation and development. Immunol Res. 1999;19:119–125. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Wang J, Sun Y, Wu Q, Fu YX. Complementary effects of TNF and lymphotoxin on the formation of germinal center and follicular dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2001;166:330–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

