Homeostatic competition among T cells revealed by conditional inactivation of the mouse Cd4 gene
- PMID: 11748274
- PMCID: PMC2193581
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1721
Homeostatic competition among T cells revealed by conditional inactivation of the mouse Cd4 gene
Abstract
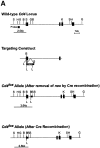
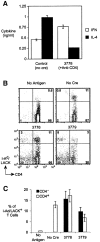
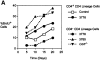
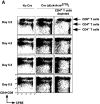
Absence of CD4 impairs the efficiency of T cell receptor (TCR) signaling in response to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-presented peptides. Here we use mice carrying a conditional Cd4 allele to study the consequences of impaired TCR signaling after the completion of thymocyte development. We show that loss of CD4 decreases the steady-state proliferation of T cells as monitored by in vivo labeling with bromo-deoxyuridine. Moreover, T cells lacking CD4 compete poorly with CD4-expressing T cells during proliferative expansion after transfer into lymphopenic recipients. The data suggest that T cells compete with one another during homeostatic proliferation, and indicate that the basis of this competition is TCR signaling.
Figures










References
-
- Takeda, S., H.R. Rodewald, H. Arakawa, H. Bluethmann, and T. Shimizu. 1996. MHC class II molecules are not required for survival of newly generated CD4+ T cells, but affect their long-term life span. Immunity. 5:217–228. - PubMed
-
- Boursalian, T.E., and K. Bottomly. 1999. Survival of naive CD4 T cells: roles of restricting versus selecting MHC class II and cytokine milieu. J. Immunol. 162:3795–3801. - PubMed
-
- Clarke, S.R., and A.Y. Rudensky. 2000. Survival and homeostatic proliferation of naive peripheral CD4+ T cells in the absence of self peptide:MHC complexes. J. Immunol. 165:2458–2464. - PubMed
-
- Rooke, R., C. Waltzinger, C. Benoist, and D. Mathis. 1997. Targeted complementation of MHC class II deficiency by intrathymic delivery of recombinant adenoviruses. Immunity. 7:123–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

