Blocking chemokine responsive to gamma-2/interferon (IFN)-gamma inducible protein and monokine induced by IFN-gamma activity in vivo reduces the pathogenetic but not the antiviral potential of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 11748277
- PMCID: PMC2193580
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1755
Blocking chemokine responsive to gamma-2/interferon (IFN)-gamma inducible protein and monokine induced by IFN-gamma activity in vivo reduces the pathogenetic but not the antiviral potential of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
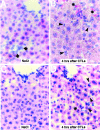
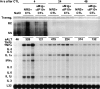
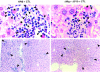
Using transgenic mice that replicate hepatitis B virus (HBV) at high levels in the liver as recipients of HBV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), we showed that the chemokines responsive to gamma-2/IFN-gamma inducible protein ([Crg2]IP-10) and monokine induced by interferon-gamma (Mig) are rapidly and strongly induced in the liver after CTL transfer. The transferred CTLs produce neither chemokine; rather, they activate (via the secretion of IFN-gamma) hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells of the liver to produce (Crg2)IP-10 and Mig. Importantly, blocking these chemokines in vivo reduces the recruitment of host-derived lymphomononuclear cells into the liver and the severity of the liver disease without affecting the IFN-gamma-dependent antiviral potential of the CTLs. The finding that neutralization of these chemokines is associated with maintenance of antiviral effects but diminished tissue damage may be significant for the development of immunotherapeutic approaches for the treatment of chronic HBV infection.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Depletion of neutrophils blocks the recruitment of antigen-nonspecific cells into the liver without affecting the antiviral activity of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99(21):13717-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172521999. Epub 2002 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12368481 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent hepatitis B viral replication in a FVB/N mouse model: impact of host and viral factors.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036984. Epub 2012 May 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615863 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-γ facilitates hepatic antiviral T cell retention for the maintenance of liver-induced systemic tolerance.J Exp Med. 2016 May 30;213(6):1079-93. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151218. Epub 2016 May 2. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27139489 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus transgenic mice: models of viral immunobiology and pathogenesis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;206:149-73. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-85208-4_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8608715 Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis.Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:29-60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.000333. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7612225 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiplatelet drug therapy moderates immune-mediated liver disease and inhibits viral clearance in mice infected with a replication-deficient adenovirus.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Nov;14(11):1532-5. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00298-07. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17881509 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of neutrophils blocks the recruitment of antigen-nonspecific cells into the liver without affecting the antiviral activity of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99(21):13717-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172521999. Epub 2002 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12368481 Free PMC article.
-
KIR and HLA loci are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with hepatitis B virus infection: a case-control study.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025682. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998681 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of P2RX7 ameliorates liver injury by reducing inflammation and fibrosis.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 3;15(6):e0234038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234038. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32492075 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Disease: Induction, Progression, Immunological Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 24;22(13):6777. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136777. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chisari, F.V., and C. Ferrari. 1995. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13:29–60. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu, Y., L.G. Guidotti, P. Fowler, and F.V. Chisari. 1998. Dendritic cell immunization breaks cytotoxic T lymphocyte tolerance in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 161:4520–4529. - PubMed
-
- Ando, K., L.G. Guidotti, S. Wirth, T. Ishikawa, G. Missale, T. Moriyama, R.D. Schreiber, H.J. Schlicht, S. Huang, and F.V. Chisari. 1994. Class I restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes are directly cytopathic for their target cells in vivo. J. Immunol. 152:3245–3253. - PubMed

