Natural killer T cell activation protects mice against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 11748281
- PMCID: PMC2193577
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1801
Natural killer T cell activation protects mice against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
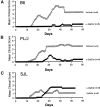
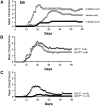
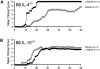
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) serves as a prototypic model for T cell-mediated autoimmunity. V(alpha)14 natural killer T (NKT) cells are a subset of T lymphocytes that recognize glycolipid antigens presented by the nonpolymorphic major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-like protein CD1d. Here, we show that activation of V(alpha)14 NKT cells by the glycosphingolipid alpha-galactosylceramide (alpha-GalCer) protects susceptible mice against EAE. beta-GalCer, which binds CD1d but is not recognized by NKT cells, failed to protect mice against EAE. Furthermore, alpha-GalCer was unable to protect CD1d knockout (KO) mice against EAE, indicating the requirement for an intact CD1d antigen presentation pathway. Protection of disease conferred by alpha-GalCer correlated with its ability to suppress myelin antigen-specific Th1 responses and/or to promote myelin antigen-specific Th2 cell responses. alpha-GalCer was unable to protect IL-4 KO and IL-10 KO mice against EAE, indicating a critical role for both of these cytokines. Because recognition of alpha-GalCer by NKT cells is phylogenetically conserved, our findings have identified NKT cells as novel target cells for treatment of inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system.
Figures

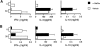
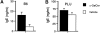
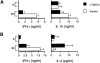
Similar articles
-
Activation of natural killer T cells potentiates or prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Exp Med. 2001 Dec 17;194(12):1789-99. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1789. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11748280 Free PMC article.
-
A subset of NKT cells that lacks the NK1.1 marker, expresses CD1d molecules, and autopresents the alpha-galactosylceramide antigen.J Immunol. 2000 Nov 1;165(9):4917-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.9.4917. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11046017
-
Regulation of immune responses by CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells.Immunol Res. 2004;30(2):139-53. doi: 10.1385/IR:30:2:139. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15477656 Review.
-
Application of natural killer T cells in antitumor immunotherapy.Crit Rev Immunol. 2007;27(6):511-25. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v27.i6.20. Crit Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18197797 Review.
-
Abrogation of Endogenous Glycolipid Antigen Presentation on Myelin-Laden Macrophages by D-Sphingosine Ameliorates the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 19;10:404. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00404. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30941120 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Different subsets of natural killer T cells may vary in their roles in health and disease.Immunology. 2014 Jul;142(3):321-36. doi: 10.1111/imm.12247. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24428389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of bacteria on the phenotype, functions, and therapeutic activities of invariant NKT cells in mice.J Clin Invest. 2008 Jun;118(6):2301-15. doi: 10.1172/JCI33071. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18451996 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in immune tolerance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008 Jan 14;60(2):91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.08.025. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008. PMID: 17976856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer T cells in multiple sclerosis and its animal model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Immunology. 2015 Sep;146(1):1-10. doi: 10.1111/imm.12485. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 26032048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct engagement of TLR4 in invariant NKT cells regulates immune diseases by differential IL-4 and IFN-γ production in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045348. Epub 2012 Sep 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinman, L. 1999. Assessment of animal models for MS and demyelinating disease in the design of rational therapy. Neuron. 24:511–514. - PubMed
-
- Powell, M.B., D. Mitchell, J. Lederman, J. Buckmeier, S.S. Zamvil, M. Graham, N.H. Ruddle, and L. Steinman. 1990. Lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-α production by myelin basic protein-specific T cell clones correlates with encephalitogenicity. Int. Immunol. 2:539–544. - PubMed
-
- Begolka, W.S., C.L. Vanderlugt, S.M. Rahbe, and S.D. Miller. 1998. Differential expression of inflammatory cytokines parallels progression of central nervous system pathology in two clinically distinct models of multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol. 161:4437–4446. - PubMed
-
- Issazadeh, S., A. Ljungdahl, B. Hojeberg, M. Mustafa, and T. Olsson. 1995. Cytokine production in the central nervous system of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: dynamics of mRNA expression for interleukin-10, interleukin-12, cytolysin, tumor necrosis factor alpha and tumor necrosis factor beta. J. Neuroimmunol. 61:205–212. - PubMed
-
- Issazadeh, S., V. Navikas, M. Schaub, M. Sayegh, and S. Khoury. 1998. Kinetics of expression of costimulatory molecules and their ligands in murine relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in vivo. J. Immunol. 161:1104–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

