The extracellular domain of CD83 inhibits dendritic cell-mediated T cell stimulation and binds to a ligand on dendritic cells
- PMID: 11748282
- PMCID: PMC2193570
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1813
The extracellular domain of CD83 inhibits dendritic cell-mediated T cell stimulation and binds to a ligand on dendritic cells
Abstract
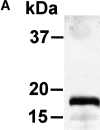
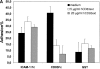
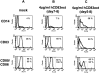
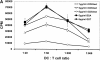
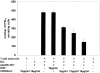
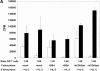
CD83 is an immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily member that is upregulated during the maturation of dendritic cells (DCs). It has been widely used as a marker for mature DCs, but its function is still unknown. To approach its potential functional role, we have expressed the extracellular Ig domain of human CD83 (hCD83ext) as a soluble protein. Using this tool we could show that immature as well as mature DCs bind to CD83. Since CD83 binds a ligand also expressed on immature DCs, which do not express CD83, indicates that binding is not a homophilic interaction. In addition we demonstrate that hCD83ext interferes with DC maturation downmodulating the expression of CD80 and CD83, while no phenotypical effects were observed on T cells. Finally, we show that hCD83ext inhibits DC-dependent allogeneic and peptide-specific T cell proliferation in a concentration dependent manner in vitro. This is the first report regarding functional aspects of CD83 and the binding of CD83 to DCs.
Figures







References
-
- Steinman, R.M. 1991. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 9:271–296. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau, J., and R.M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 392:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Zhou, L.J., R. Schwarting, H.M. Smith, and T.F. Tedder. 1992. A novel cell-surface molecule expressed by human interdigitating reticulum cells, Langerhans cells, and activated lymphocytes is a new member of the Ig superfamily. J. Immunol. 149:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Kozlow, E.J., G.L. Wilson, C.H. Fox, and J.H. Kehrl. 1993. Subtractive cDNA cloning of a novel member of the Ig gene superfamily expressed at high levels in activated B lymphocytes. Blood. 81:454–461. - PubMed

