Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells
- PMID: 11748286
- PMCID: PMC2193582
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1861
Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells
Abstract
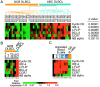
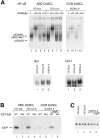
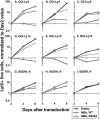
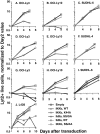
Gene expression profiling has revealed that diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) consists of at least two distinct diseases. Patients with one DLBCL subtype, termed activated B cell-like (ABC) DLBCL, have a distinctly inferior prognosis. An untapped potential of gene expression profiling is its ability to identify pathogenic signaling pathways in cancer that are amenable to therapeutic attack. The gene expression profiles of ABC DLBCLs were notable for the high expression of target genes of the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB transcription factors, raising the possibility that constitutive activity of the NF-kappaB pathway may contribute to the poor prognosis of these patients. Two cell line models of ABC DLBCL had high nuclear NF-kappaB DNA binding activity, constitutive IkappaB kinase (IKK) activity, and rapid IkappaB(alpha) degradation that was not seen in cell lines representing the other DLBCL subtype, germinal center B-like (GCB) DLBCL. Retroviral transduction of a super-repressor form of IkappaBalpha or dominant negative forms of IKKbeta was toxic to ABC DLBCL cells but not GCB DLBCL cells. DNA content analysis showed that NF-kappaB inhibition caused both cell death and G1-phase growth arrest. These findings establish the NF-kappaB pathway as a new molecular target for drug development in the most clinically intractable subtype of DLBCL and demonstrate that the two DLBCL subtypes defined by gene expression profiling utilize distinct pathogenetic mechanisms.
Figures






References
-
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. 1996. The NF-κB and I κB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:649–683. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh, S., M.J. May, and E.B. Kopp. 1998. NF-κB and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Karin, M., and Y. Ben-Neriah. 2000. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:621–663. - PubMed
-
- Siebenlist, U., G. Franzoso, and K. Brown. 1994. Structure, regulation and function of NF-κB. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10:405–455. - PubMed
-
- Gugasyan, R., R. Grumont, M. Grossmann, Y. Nakamura, T. Pohl, D. Nesic, and S. Gerondakis. 2000. Rel/NF-κB transcription factors: key mediators of B-cell activation. Immunol. Rev. 176:134–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

