Antifungal efficacy of caspofungin (MK-0991) in experimental pulmonary aspergillosis in persistently neutropenic rabbits: pharmacokinetics, drug disposition, and relationship to galactomannan antigenemia
- PMID: 11751105
- PMCID: PMC127008
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.1.12-23.2002
Antifungal efficacy of caspofungin (MK-0991) in experimental pulmonary aspergillosis in persistently neutropenic rabbits: pharmacokinetics, drug disposition, and relationship to galactomannan antigenemia
Abstract
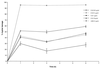
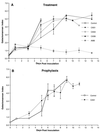
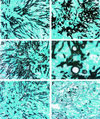
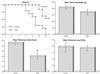
The antifungal efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety of caspofungin (CAS) were investigated in the treatment and prophylaxis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis due to Aspergillus fumigatus in persistently neutropenic rabbits. Antifungal therapy consisted of 1, 3, or 6 mg of CAS/kg of body weight/day (CAS1, CAS3, and CAS6, respectively) or 1 mg of deoxycholate amphotericin B (AMB)/kg/day intravenously for 12 days starting 24 h after endotracheal inoculation. Prophylaxis (CAS1) was initiated 4 days before endotracheal inoculation. Rabbits treated with CAS had significant improvement in survival and reduction in organism-mediated pulmonary injury (OMPI) measured by pulmonary infarct score and total lung weight (P < 0.01). However, animals treated with CAS demonstrated a paradoxical trend toward increased residual fungal burden (log CFU per gram) and increased serum galactomannan antigen index (GMI) despite improved survival. Rabbits receiving prophylactic CAS1 also showed significant improvement in survival and reduction in OMPI (P < 0.01), but there was no effect on residual fungal burden. In vitro tetrazolium salt hyphal damage assays and histologic studies demonstrated that CAS had concentration- and dose-dependent effects on hyphal structural integrity. In parallel with a decline in GMI, AMB significantly reduced the pulmonary tissue burden of A. fumigatus (P < or = 0.01). The CAS1, CAS3, and CAS6 dose regimens demonstrated dose-proportional exposure and maintained drug levels in plasma above the MIC for the entire 24-h dosing interval at doses that were > or =3 mg/kg/day. As serial galactomannan antigen levels may be used for therapeutic monitoring, one should be aware that profoundly neutropenic patients receiving echinocandins for aspergillosis might have persistent galactomannan antigenemia despite clinical improvement. CAS improved survival, reduced pulmonary injury, and caused dose-dependent hyphal damage but with no reduction in residual fungal burden or galactomannan antigenemia in persistently neutropenic rabbits with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.
Figures


References
-
- Abruzzo, G. K., A. M. Flattery, C. J. Gill, L. Kong, J. G. Smith, V. B. Pikounis, J. M. Balkovec, A. F. Bouffard, J. F. Dropinski, H. Rosen, H. Kropp, and K. Bartizal. 1997. Evaluation of the echinocandin antifungal MK-0991 (L-743,872): efficacies in mouse models of disseminated aspergillosis, candidiasis, and cryptococcosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:2333–2338. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abruzzo, G. K., C. J. Gill, A. M. Flattery, L. Kong, C. Leighton, J. G. Smith, V. B. Pikounis, K. Bartizal, and H. Rosen. 2000. Efficacy of the echinocandin caspofungin against disseminated aspergillosis and candidiasis in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:2310–2318. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anaissie, E. 1992. Opportunistic mycoses in the immunocompromised host: experience at a cancer center and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 14(Suppl. 1):S43–S53. - PubMed
-
- Barchiesi, F., A. M. Schimizzi, A. W. Fothergill, G. Scalise, and M. G. Rinaldi. 1999. In vitro activity of the new echinocandin antifungal, MK-0991, against common and uncommon clinical isolates of Candida species. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 18:302–304. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

