Conversion of oxacillin-resistant staphylococci from heterotypic to homotypic resistance expression
- PMID: 11751106
- PMCID: PMC126971
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.1.24-30.2002
Conversion of oxacillin-resistant staphylococci from heterotypic to homotypic resistance expression
Abstract
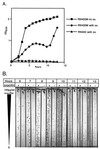
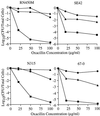
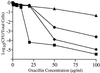
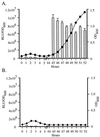
Staphylococci that acquire the mecA gene are usually resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics (methicillin or oxacillin resistance). mecA encodes a penicillin-binding protein (PBP 2a) that has a reduced affinity for beta-lactams. In some isolates with methicillin or oxacillin resistance, only a small proportion (< or =0.1%) of the population expresses resistance to > or =10 microg of oxacillin per ml (heterotypic resistance [HeR]), while in other isolates most of the population expresses resistance (homotypic resistance [HoR]). In the present study, growth of Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis strains with HeR in concentrations of oxacillin (0.3 to 0.7 microg/ml) that produced a fall or a lag in optical density converted the strains from the HeR to the HoR phenotype. The conversion from the HeR to the HoR phenotype appeared to be due to the selection of a highly resistant mutant population, as determined by fluctuation analysis and the failure of populations with HoR to revert to HeR after 60 generations of growth in antibiotic-free media. The frequencies of conversion were as high as 10(-3) to 10(-2). Conversion to HoR required an intact mecA gene and an increase in the level of mecA transcription since no highly resistant subpopulation could be selected after growth in oxacillin when mecA transcription was constitutively repressed or when mecA had been inactivated. In addition, in both S. epidermidis and S. aureus the level of resistance to vancomycin, which also acts directly on the staphylococcal cell wall, was greater among convertants with HoR than their isogenic parents. The conversion of a population from HeR to HoR involves the selection of a mutation(s) that occurs at a high frequency and most likely requires abundant PBP 2a.
Figures
References
-
- Berger-Bachi, B., and M. Tschierske. 1998. Role of Fem factors in methicillin resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 1:325–335. - PubMed
-
- Boudewijn, L. M., B. L. de Jonge, and A. Tomasz. 1993. Abnormal peptidoglycan produced in a methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus gown in the presence of methicillin: functional role for penicillin-binding protein 2A in cell wall synthesis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37:342–346. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

