SEK-1 MAPKK mediates Ca2+ signaling to determine neuronal asymmetric development in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 11751572
- PMCID: PMC1083920
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf001
SEK-1 MAPKK mediates Ca2+ signaling to determine neuronal asymmetric development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
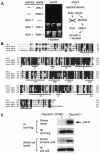
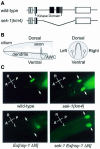
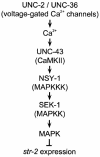
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a highly conserved signaling cascade that converts extracellular signals into various outputs. In Caenorhabditis elegans, asymmetric expression of the candidate odorant receptor STR-2 in either the left or the right of two bilaterally symmetrical olfactory AWC neurons is regulated by axon contact and Ca2+ signaling. We show that the MAPK kinase (MAPKK) SEK-1 is required for asymmetric expression in AWC neurons. Genetic and biochemical analyses reveal that SEK-1 functions in a pathway downstream of UNC-43 and NSY-1, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and MAPK kinase kinase (MAPKKK), respectively. Thus, the NSY-1-SEK-1-MAPK cascade is activated by Ca2+ signaling through CaMKII and establishes asymmetric cell fate decision during neuronal development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The CaMKII UNC-43 activates the MAPKKK NSY-1 to execute a lateral signaling decision required for asymmetric olfactory neuron fates.Cell. 2001 Apr 20;105(2):221-32. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00313-0. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11336672
-
Noncell- and cell-autonomous G-protein-signaling converges with Ca2+/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling to regulate str-2 receptor gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2006 Jul;173(3):1287-99. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.058750. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16868120 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple p38/JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways mediate salt chemotaxis learning in C. elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Aug 30;13(9):jkad129. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad129. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 37310929 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic left-right neuronal asymmetry in Caenorhabditis elegans.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Dec 19;371(1710):20150407. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0407. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27821536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of MAP kinase cascades in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Biochem. 2004 Jul;136(1):7-11. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh097. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15269234 Review.
Cited by
-
A Defensin from the Model Beetle Tribolium castaneum Acts Synergistically with Telavancin and Daptomycin against Multidrug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 10;10(6):e0128576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128576. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26062137 Free PMC article.
-
A CaMK cascade activates CRE-mediated transcription in neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans.EMBO Rep. 2002 Oct;3(10):962-6. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf191. Epub 2002 Sep 13. EMBO Rep. 2002. PMID: 12231504 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model to Study the Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms of Drug Addiction.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016;137:229-52. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.10.019. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016. PMID: 26810004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput screen for novel antimicrobials using a whole animal infection model.ACS Chem Biol. 2009 Jul 17;4(7):527-33. doi: 10.1021/cb900084v. ACS Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19572548 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing salicylanilide anthelmintic drugs to combat drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 21;10(4):e0124595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124595. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25897961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Derijard B., Raingeaud, J., Barrett, T., Wu, I.H., Han, J., Ulevitch, R.J. and Davis, R.J. (1995) Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science, 267, 682–685. - PubMed
-
- Ichijo H. et al. (1997) Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science, 275, 90–94. - PubMed
-
- Ip Y.T. and Davis, R.J. (1998). Signal transduction by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) from inflammation to development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 10, 205–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

