HAT activity is essential for CBP-1-dependent transcription and differentiation in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 11751575
- PMCID: PMC1083925
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf006
HAT activity is essential for CBP-1-dependent transcription and differentiation in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
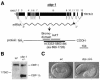
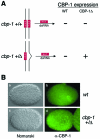
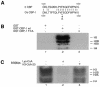
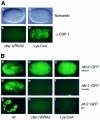
The p300/CBP family of transcriptional coactivators possesses multiple functional domains, including a histone acetyltransferase (HAT) and several activation domains. A number of models have been proposed to account for their roles in transcriptional activation, including interactions with basal transcription machinery and chromatin remodeling. However, individual contributions of these domains to transcriptional activation and their significance in living organisms remain unclear. We addressed the importance of the HAT activity of CBP-1, the worm ortholog of p300/CBP, in Caenorhabditis elegans with three different and complementary approaches. These include allele-specific RNA-mediated interference (RNAi), genetic rescue and the use of a specific chemical inhibitor of the p300/CBP HAT. Our findings demonstrate that HAT activity is of primary importance for CBP-1 to regulate transcription and to promote differentiation during C. elegans embryogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A CBP/p300 homolog specifies multiple differentiation pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genes Dev. 1998 Apr 1;12(7):943-55. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.7.943. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9531533 Free PMC article.
-
A gain-of-function allele of cbp-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog of the mammalian CBP/p300 gene, causes an increase in histone acetyltransferase activity and antagonism of activated Ras.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;25(21):9427-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.21.9427-9434.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16227593 Free PMC article.
-
The histone acetyltransferase domains of CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300/CBP-associated factor are not necessary for cooperativity with the class II transactivator.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):38715-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106652200. Epub 2001 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11514574
-
Transcriptional/epigenetic regulator CBP/p300 in tumorigenesis: structural and functional versatility in target recognition.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Nov;70(21):3989-4008. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1254-4. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23307074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein lysine acetyltransferase CBP/p300: A promising target for small molecules in cancer treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Feb;171:116130. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116130. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38215693 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of allele-specific gene silencing by RNA interference with mutant and wild-type reporter alleles.J RNAi Gene Silencing. 2006 Feb 28;2(1):154-60. J RNAi Gene Silencing. 2006. PMID: 19771217 Free PMC article.
-
Lifespan-increasing drug nordihydroguaiaretic acid inhibits p300 and activates autophagy.NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2019 Oct 2;5:7. doi: 10.1038/s41514-019-0037-7. eCollection 2019. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2019. PMID: 31602311 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of allele discrimination by introduction of nucleotide mismatches into siRNA in allele-specific gene silencing by RNAi.PLoS One. 2008 May 21;3(5):e2248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002248. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18493311 Free PMC article.
-
Systems-level quantification of division timing reveals a common genetic architecture controlling asynchrony and fate asymmetry.Mol Syst Biol. 2015 Jun 10;11(6):814. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145857. Mol Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26063786 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine Acetyltransferase p300/CBP Plays an Important Role in Reproduction, Embryogenesis and Longevity of the Pea Aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum.Insects. 2020 Apr 26;11(5):265. doi: 10.3390/insects11050265. Insects. 2020. PMID: 32357443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister A.J. and Kouzarides, T. (1996) The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature, 384, 641–643. - PubMed
-
- Barstead R.J. (1999) Reverse genetics. In Hope, I.A. (ed.), C. elegans: A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, pp. 97–118.
-
- Brownell J.E. and Allis, C.D. (1996) Special HATs for special occasions: linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 6, 176–184. - PubMed
-
- Epstein H.F. and Shakes, D.C. (eds) (1995) Methods in Cell Biology. Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

