Mediator function of the human Rad51B-Rad51C complex in Rad51/RPA-catalyzed DNA strand exchange
- PMID: 11751636
- PMCID: PMC312844
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.935501
Mediator function of the human Rad51B-Rad51C complex in Rad51/RPA-catalyzed DNA strand exchange
Abstract
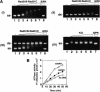
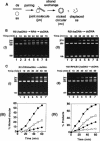
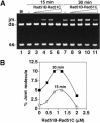
Five Rad51-like proteins, referred to as Rad51 paralogs, have been described in vertebrates. We show that two of them, Rad51B and Rad51C, are associated in a stable complex. Rad51B-Rad51C complex has ssDNA binding and ssDNA-stimulated ATPase activities. We also examined the functional interaction of Rad51B-Rad51C with Rad51 and RPA. Even though RPA enhances Rad51-catalyzed DNA joint formation via removal of secondary structure in the ssDNA substrate, it can also compete with Rad51 for binding to the substrate, leading to suppressed reaction efficiency. The competition by RPA for substrate binding can be partially alleviated by Rad51B-Rad51C. This recombination mediator function of Rad51B-Rad51C is likely required for the assembly of the Rad51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filament in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- ————— Heteroduplex formation by human Rad51 protein: Effects of DNA end-structure, hRP-A and hRad52. J Mol Biol. 1999;291:363–374. - PubMed
-
- Beernink HT, Morrical SW. RMPs: Recombination/replication mediator proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:385–389. - PubMed
-
- Bianco PR, Tracy RB, Kowalczykowski SC. DNA strand exchange proteins: A biochemical and physical comparison. Front Biosci. 1998;3:D570–D603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
