Chromatin-specific regulation of LEF-1-beta-catenin transcription activation and inhibition in vitro
- PMID: 11751639
- PMCID: PMC312851
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.946501
Chromatin-specific regulation of LEF-1-beta-catenin transcription activation and inhibition in vitro
Abstract
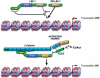
Transcriptional activation of Wnt/Wg-responsive genes requires the stabilization and nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin, a dedicated coactivator of LEF/TCF enhancer-binding proteins. Here we report that recombinant beta-catenin strongly enhances binding and transactivation by LEF-1 on chromatin templates in vitro. Interestingly, different LEF-1 isoforms vary in their ability to bind nucleosomal templates in the absence of beta-catenin, owing to N-terminal residues that repress binding to chromatin, but not nonchromatin, templates. Transcriptional activation in vitro requires both the armadillo (ARM) repeats and the C terminus of beta-catenin, whereas the phosphorylated N terminus is inhibitory to transcription. A fragment spanning the C terminus (CT) and ARM repeats 11 and 12 (CT-ARM), but not the CT alone, functions as a dominant negative inhibitor of LEF-1-beta-cat activity in vitro and can block ATP-dependent binding of the complex to chromatin. LEF-1-beta-cat transactivation in vitro was also repressed by inhibitor of beta-catenin and Tcf-4 (ICAT), a physiological inhibitor of Wnt/Wg signaling that interacts with ARM repeats 11 and 12, and by the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory compound, sulindac. None of these transcription inhibitors (CT-ARM, ICAT, or sulindac) could disrupt the LEF-1-beta-cat complex after it was stably bound to chromatin. We conclude that the CT-ARM region of beta-catenin functions as a chromatin-specific activation domain, and that several inhibitors of the Wnt/Wg pathway directly modulate LEF-1-beta-cat activity on chromatin.
Figures

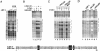

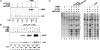

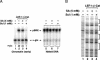
Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between Rac1 GTPase and dysregulated Wnt signaling pathway leads to cellular redistribution of beta-catenin and TCF/LEF-mediated transcriptional activation.Oncogene. 2004 Oct 28;23(50):8260-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208007. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15377999
-
Regulation of lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T-cell factor by mitogen-activated protein kinase-related Nemo-like kinase-dependent phosphorylation in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;23(4):1379-89. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1379-1389.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12556497 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-catenin can act as a nuclear import receptor for its partner transcription factor, lymphocyte enhancer factor-1 (lef-1).Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):357-63. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.05.011. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15936755
-
Wnt signalling: a theme with nuclear variations.Bioessays. 2001 Apr;23(4):311-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.1045. Bioessays. 2001. PMID: 11268036 Review.
-
Signaling through beta-catenin and Lef/Tcf.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Oct 30;56(5-6):523-37. doi: 10.1007/s000180050449. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 11212302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SMADs and YAP compete to control elongation of β-catenin:LEF-1-recruited RNAPII during hESC differentiation.Mol Cell. 2015 Jun 4;58(5):780-93. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25936800 Free PMC article.
-
Why Is Wnt/β-Catenin Not Yet Targeted in Routine Cancer Care?Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;17(7):949. doi: 10.3390/ph17070949. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cdx1 autoregulation is governed by a novel Cdx1-LEF1 transcription complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jun;24(11):5028-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.5028-5038.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15143193 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cells and TCF proteins: a role for beta-catenin--independent functions.Stem Cell Rev. 2007 Jan;3(1):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s12015-007-0003-9. Stem Cell Rev. 2007. PMID: 17873380 Review.
-
LEF1 enhances β-catenin transactivation through IDR-dependent liquid-liquid phase separation.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Sep 1;6(11):e202302118. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302118. Print 2023 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37657935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong JA, Bieker JJ, Emerson BM. A SWI/SNF-related chromatin remodeling complex, E-RC1, is required for tissue-specific transcriptional regulation by EKLF in vitro. Cell. 1998;95:93–104. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1996;382:638–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
