Reference standards, judges, and comparison subjects: roles for experts in evaluating system performance
- PMID: 11751799
- PMCID: PMC349383
- DOI: 10.1136/jamia.2002.0090001
Reference standards, judges, and comparison subjects: roles for experts in evaluating system performance
Abstract
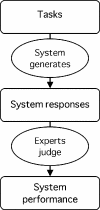
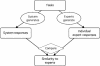
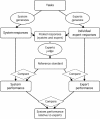
Medical informatics systems are often designed to perform at the level of human experts. Evaluation of the performance of these systems is often constrained by lack of reference standards, either because the appropriate response is not known or because no simple appropriate response exists. Even when performance can be assessed, it is not always clear whether the performance is sufficient or reasonable. These challenges can be addressed if an evaluator enlists the help of clinical domain experts. 1) The experts can carry out the same tasks as the system, and then their responses can be combined to generate a reference standard. 2)The experts can judge the appropriateness of system output directly. 3) The experts can serve as comparison subjects with which the system can be compared. These are separate roles that have different implications for study design, metrics, and issues of reliability and validity. Diagrams help delineate the roles of experts in complex study designs.
Figures




Comment in
-
Reference standards in evaluating system performance.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2002 Jan-Feb;9(1):87-8. doi: 10.1136/jamia.2002.0090087. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2002. PMID: 11751807 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Reference standards in evaluating system performance.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2002 Jan-Feb;9(1):87-8. doi: 10.1136/jamia.2002.0090087. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2002. PMID: 11751807 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A reliability study for evaluating information extraction from radiology reports.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1999 Mar-Apr;6(2):143-50. doi: 10.1136/jamia.1999.0060143. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1999. PMID: 10094067 Free PMC article.
-
A framework for evaluation of medical information systems.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2003;95:611-6. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2003. PMID: 14664055
-
[Diagnostic kits in parasitology: which controls?].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):145-9. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305705 Review. Italian.
-
Setting the informatics standards: an overview of NIDSEC's information systems evaluation criteria.Nurs Econ. 1998 Sep-Oct;16(5):279-81, 278. Nurs Econ. 1998. PMID: 9987329 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Building and evaluation of a structured representation of pharmacokinetics information presented in SPCs: from existing conceptual views of pharmacokinetics associated with natural language processing to object-oriented design.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003 May-Jun;10(3):271-80. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1193. Epub 2003 Jan 28. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003. PMID: 12626375 Free PMC article.
-
Human and automated coding of rehabilitation discharge summaries according to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006 Sep-Oct;13(5):508-15. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2107. Epub 2006 Jun 23. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006. PMID: 16799117 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Development of an Automated Platform for Assessing Trainee Performance on Case Presentations.ATS Sch. 2022 Sep 23;3(4):548-560. doi: 10.34197/ats-scholar.2022-0010OC. eCollection 2022 Dec. ATS Sch. 2022. PMID: 36726701 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learned in replicating data-driven experiments in multiple medical systems and patient populations.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2013 Nov 16;2013:786-95. eCollection 2013. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2013. PMID: 24551375 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the impact of diagnostic decision support on the quality of clinical decision making: development of a reliable and valid composite score.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003 Nov-Dec;10(6):563-72. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1338. Epub 2003 Aug 4. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003. PMID: 12925549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman CP, Wyatt JC. Evaluation Methods in Medical Informatics. New York: Springer, 1997.
-
- Willems JL, Abreu-Lima C, Arnaud P, et al. Evaluation of ECG interpretation results obtained by computer and cardiologists. Methods Inf Med. 1990;29:308–16. - PubMed
-
- Miller PL. Issues in the evaluation of artificial intelligence systems in medicine. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med Care. 1985:281–6.
-
- Willems JL, Abreu-Lima C, Arnaud P, et al. The diagnostic performance of computer programs for the interpretation of electrocardiograms. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1767–73. - PubMed
-
- Michaelis J, Wellek S, Willems JL. Reference standards for software evaluation. Methods Inf Med. 1990;29:289–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

