VmrA, a member of a novel class of Na(+)-coupled multidrug efflux pumps from Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- PMID: 11751837
- PMCID: PMC139572
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.2.572-576.2002
VmrA, a member of a novel class of Na(+)-coupled multidrug efflux pumps from Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Abstract
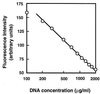
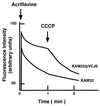
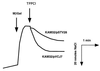
Gene vmrA, cloned from Vibrio parahaemolyticus, made Escherichia coli resistant to 4',6-diamino-2-phenylindol, tetraphenylphosphonium chloride, acriflavine, and ethidium bromide. VmrA belongs to the DinF branch of MATE family efflux transporters. VmrA catalyzed acriflavine efflux and showed Na(+)/drug transporter activity because the addition of tetraphenylphosphonium to Na(+)-loaded cells caused Na(+) efflux.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gene cloning and characterization of VcrM, a Na+-coupled multidrug efflux pump, from Vibrio cholerae non-O1.Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47(6):419-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03379.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12906102
-
NorM, a putative multidrug efflux protein, of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its homolog in Escherichia coli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998 Jul;42(7):1778-82. doi: 10.1128/AAC.42.7.1778. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998. PMID: 9661020 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of the HmrM multidrug efflux pump from Haemophilus influenzae Rd.Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47(12):937-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03467.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14695443
-
Precious things come in little packages.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Apr;3(2):155-62. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11321568 Review.
-
Sodium or potassium efflux ATPase a fungal, bryophyte, and protozoal ATPase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct;1798(10):1841-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.07.009. Epub 2010 Jul 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20650263 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the High-affinity Substrate-binding Site of the Multidrug and Toxic Compound Extrusion (MATE) Family Transporter from Pseudomonas stutzeri.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 22;291(30):15503-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.728618. Epub 2016 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27235402 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of antibacterial compounds with RND efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jul 8;6:660. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00660. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26217310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of MATE-type multidrug efflux pumps from Klebsiella pneumoniae MGH78578.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 25;10(3):e0121619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121619. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25807080 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved binding site in the N-lobe of prokaryotic MATE transporters suggests a role for Na+ in ion-coupled drug efflux.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100262. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100262. Epub 2021 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33837745 Free PMC article.
-
MATE transport of the E. coli-derived genotoxin colibactin.Nat Microbiol. 2016 Jan 11;1:15009. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2015.9. Nat Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27571755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atsumi, T., L. McCarter, and Y. Imae. 1992. Polar and lateral flagellar motors of marine Vibrio are driven by different ion-motive forces. Nature 355:182–184. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, P., and R. H. W. Schubert. 1984. Family II: Vibrionaceae veron, p.516–550. In S. T. Williams, M. E. Sharpe, and J. G. Holt (ed.), Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol. 1. The Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, Md.
-
- Berns, K. L., and C. A. J. Thomas. 1965. Isolation of high molecular weight DNA from Haemophilus influenzae. J. Mol. Biol. 11:476–490. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. H., I. T. Paulsen, and R. A. Skurray. 1999. The multidrug efflux protein NorM is a prototype of a new family of transporters. Mol. Microbiol. 31:394–395. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg, D., E. Schwarz, M. Komaromy, and R. Wall. 1984. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J. Mol. Biol. 179:125–142. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

