Structure-function relationships of the raloxifene-estrogen receptor-alpha complex for regulating transforming growth factor-alpha expression in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 11751902
- PMCID: PMC3696956
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M108335200
Structure-function relationships of the raloxifene-estrogen receptor-alpha complex for regulating transforming growth factor-alpha expression in breast cancer cells
Abstract
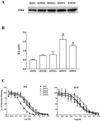
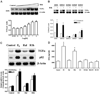
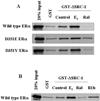
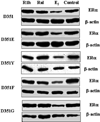
Amino acid Asp-351 in the ligand binding domain of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) plays an important role in regulating the estrogen-like activity of selective estrogen receptor modulator-ERalpha complexes. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen is a full agonist at a transforming growth factor alpha target gene in situ in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells stably transfected with the wild-type ERalpha. In contrast, raloxifene (Ral), which is also a selective estrogen receptor modulator, is a complete antiestrogen in this system. Because D351G ERalpha allosterically silences activation function-1 activity in the 4-hydroxytamoxifen-ERalpha complex with the complete loss of estrogen-like activity, we examined the converse interaction of amino acid 351 and the piperidine ring of the antiestrogen side chain of raloxifene to enhance estrogen-like action. MDA-MB-231 cells were either transiently or stably transfected with Asp-351 (the wild type), D351E, D351Y, or D351F ERalpha expression vectors. Profound differences in the agonist and antagonist actions of Ralcenter dotERalpha complexes were noted only in stable transfectants. The agonist activity of the Ralcenter dotERalpha complex was enhanced with D351E and D351Y ERalpha, but raloxifene lost its agonist activity with D351F ERalpha. The distance between the piperidine nitrogen of raloxifene and the negative charge of amino acid 351 was critical for estrogen-like actions. The role of the piperidine ring in neutralizing Asp-351 was addressed using compound R1h, a raloxifene derivative replacing the nitrogen on its piperidine ring with a carbon to form cyclohexane. The derivative was a potent agonist with wild type ERalpha. These results support the concept that the side chain of raloxifene shields and neutralizes the Asp-351 to produce an antiestrogenic ERalpha complex. Alteration of either the side chain or its relationship with the negative charge at amino acid 351 controls the estrogen-like action at activating function 2b of the selective estrogen receptor modulator ERalpha complex.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Silencing and reactivation of the selective estrogen receptor modulator-estrogen receptor alpha complex.Cancer Res. 2001 May 1;61(9):3632-9. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11325832
-
Molecular mechanism of action at estrogen receptor alpha of a new clinically relevant antiestrogen (GW7604) related to tamoxifen.Endocrinology. 2001 Feb;142(2):838-46. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.2.7932. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11159857
-
Allosteric silencing of activating function 1 in the 4-hydroxytamoxifen estrogen receptor complex is induced by substituting glycine for aspartate at amino acid 351.Cancer Res. 2000 Sep 15;60(18):5097-105. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 11016635
-
Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000 Nov 30;74(5):279-85. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(00)00104-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11162936 Review.
-
Tamoxifen to raloxifene and beyond.Semin Oncol. 2001 Jun;28(3):260-73. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2001.23492. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11402436 Review.
Cited by
-
Acquired resistance to selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) in clinical practice (tamoxifen & raloxifene) by selection pressure in breast cancer cell populations.Steroids. 2014 Nov;90:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Steroids. 2014. PMID: 24930824 Free PMC article.
-
The new biology of estrogen-induced apoptosis applied to treat and prevent breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Feb;22(1):R1-31. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0448. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25339261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural underpinnings of oestrogen receptor mutations in endocrine therapy resistance.Nat Rev Cancer. 2018 Jun;18(6):377-388. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0001-z. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29662238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by raloxifene and estrogen in human endometrial stromal ThESC cell line.Arch Med Sci. 2017 Mar 1;13(2):293-301. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.59874. Epub 2016 May 12. Arch Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28261281 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Induction of the Unfolded Protein Response and Apoptosis by Estrogen Mimic TTC-352 for the Treatment of Endocrine-Resistant Breast Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Jan;20(1):11-25. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0563. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 33177154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black LJ, Jones CD, Falcone JF. Life Sci. 1983;32:1031–1036. - PubMed
-
- Buzdar AU, Marcus C, Holmes F, Hug V, Hortobagyi G. Oncology (Basel) 1988;45:344–345. - PubMed
-
- Snyder KR, Sparano N, Malinowski JM. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharmacol. 2000;57:1669–1678. - PubMed
-
- Jordan VC, Phelps E, Lindgren JU. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1987;10:31–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

