A soluble factor(s) secreted from CD8(+) T lymphocytes inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication through STAT1 activation
- PMID: 11752148
- PMCID: PMC136805
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.2.569-581.2002
A soluble factor(s) secreted from CD8(+) T lymphocytes inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication through STAT1 activation
Abstract
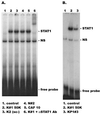
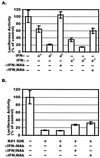
CD8(+) T lymphocytes can suppress human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) replication by secreting a soluble factor(s) known as CD8(+) T-lymphocyte antiviral factor (CAF). One site of CAF action is inhibition of HIV-1 RNA transcription, particularly at the step of long terminal repeat (LTR)-driven gene expression. However, the mechanism by which CAF inhibits LTR activation is not understood. Here, we show that conditioned media from several herpesvirus saimari-transformed CD8(+) T lymphocytes inhibit, in a time- and dose-dependent manner, the replication of HIV-1 pseudotype viruses that express the envelope glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus (HIV-1(VSV)). The same conditioned media also inhibit phorbol myristate acetate-induced activation of the HIV-1 LTR and activate the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) protein. We have obtained direct evidence that STAT1 is necessary for CAF-mediated inhibition of LTR activation and HIV-1 replication. Thus, the inhibitory effect of CAF on HIV-1(VSV) replication was abolished in STAT1-deficient cells. Moreover, CAF inhibition of LTR activation was diminished both in STAT1-deficient cells and in cells expressing a STAT1 dominant negative mutant but was restored when STAT1 was reintroduced into the STAT1-deficient cells. We also observed that CAF induced the expression of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1), and that IRF-1 gene induction was STAT-1 dependent. Taken together, our results suggest that CAF activates STAT1, leading to IRF-1 induction and inhibition of gene expression regulated by the HIV-1 LTR. This study therefore helps clarify one molecular mechanism of host defense against HIV-1.
Figures






References
-
- Bailer, R. T., A. Holloway, J. Sun, J. B. Margolick, M. Martin, J. Kostman, and L. J. Montaner. 1999. IL-13 and IFN-gamma secretion by activated T cells in HIV-1 infection associated with viral suppression and a lack of disease progression. J. Immunol. 162:7534–7542. - PubMed
-
- Benkirane, M., R. F. Chun, H. Xiao, V. V. Ogryzko, B. H. Howard, Y. Nakatani, and K. T. Jeang. 1998. Activation of integrated provirus requires histone acetyltransferase: p300 and P/CAF are coactivators for HIV-1 Tat. J. Biol. Chem. 273:24898–24905. - PubMed
-
- Bovolenta, C., L. Camorali, A. L. Lorini, S. Ghezzi, E. Vicenzi, A. Lazzarin, and G. Poli. 1999. Constitutive activation of STATs upon in vivo human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood 94:4202–4209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

