Regions of the herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript that protect cells from apoptosis in vitro and protect neuronal cells in vivo
- PMID: 11752162
- PMCID: PMC136840
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.2.717-729.2002
Regions of the herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript that protect cells from apoptosis in vitro and protect neuronal cells in vivo
Abstract
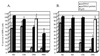
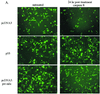
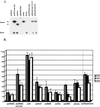
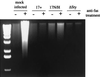
Recent studies have suggested that the latency-associated transcript (LAT) region of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is effective at blocking virus-induced apoptosis both in vitro and in the trigeminal ganglia of acutely infected rabbits (Inman et al., J. Virol. 75:3636-3646, 2001; Perng et al., Science 287:1500-1503, 2000). By transfecting cells with a construct expressing the Pst-Mlu segment of the LAT, encompassing the LAT exon 1, the stable 2.0-kb intron, and 5' part of exon 2, we confirmed that this region was able to diminish the onset of programmed cell death initiated by anti-Fas and camptothecin treatment. In addition, caspase 8-induced apoptosis was specifically inhibited in cells expressing the Pst-Mlu LAT fragment. To further delineate the minimal region of LAT that is necessary for this antiapoptotic function, LAT mutants were used in our cotransfection assays. In HeLa cells, the plasmids lacking exon sequences were the least effective at blocking apoptosis. However, similar to previous work (Inman et al., op. cit.), our data also indicated that the 5' end of the stable 2.0-kb LAT intron appeared to contribute to the promotion of cell survival. Furthermore, cells productively infected with the 17N/H LAT mutant virus, a virus deleted in the LAT promoter, exon 1, and about half of the intron, exhibited a greater degree of DNA fragmentation than cells infected with wild-type HSV-1. These data support the finding that the exon 1 and 2.0-kb intron region of the LAT transcription unit display an antiapoptotic function both in transfected cells and in the context of the virus infection in vitro. In trigeminal ganglia of mice acutely infected with the wild-type virus, 17, and 17DeltaSty, a virus lacking most of exon 1, apoptosis was not detected in cells that were positive for virus particles. However, dual staining was observed in cells from mice infected with 17N/H virus, indicating that the LAT antiapoptotic function demonstrated in cells transfected by LAT-expressing constructs may also play a role in protecting cells from virus-induced apoptosis during acute viral infection in vivo.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

