FANTOM DB: database of Functional Annotation of RIKEN Mouse cDNA Clones
- PMID: 11752270
- PMCID: PMC99137
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/30.1.116
FANTOM DB: database of Functional Annotation of RIKEN Mouse cDNA Clones
Abstract
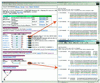
FANTOM DB, the database of Functional Annotation of RIKEN Mouse cDNA Clones, is designed to store sequence information of RIKEN full-length enriched mouse cDNA clones, graphical views of sequence analysis results, curated functional annotation information and additional descriptions, including Gene Ontology terms. RIKEN's Mouse Gene Encyclopedia Project aims to collect full-length enriched cDNA clones from various mouse tissues, determine the full-length nucleotide sequences, infer their chromosomal locations by computer and characterize gene expression patterns. FANTOM DB has been developed to facilitate this work and to facilitate functional genomic studies such as positional candidate cloning, cDNA microarrays and protein interaction analyses. FANTOM DB contains 21 076 full-length cDNA sequences with rich functional annotations and is publicly available. FANTOM DB thus provides curated functional annotation to RIKEN full-length enriched mouse clones, and has links to other public resources. FANTOM DB can be accessed at http://fantom.gsc.riken.go.jp/db/.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

