READ: RIKEN Expression Array Database
- PMID: 11752296
- PMCID: PMC99103
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/30.1.211
READ: RIKEN Expression Array Database
Abstract
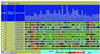
READ, the RIKEN Expression Array Database, is a database of expression profile data from the RIKEN mouse cDNA microarray. It stores the microarray experimental data and information, and provides Web interfaces for researchers to use to retrieve, analyze and display their data. The goals for READ are to serve as a storage site for microarray data from ongoing research in the RIKEN mouse encyclopedia project and to provide useful links and tools to decipher biologically important information. The gene information is based mainly on the fully annotated FANTOM database. READ can be accessed at http://read.gsc.riken.go.jp/. READ also provides a search tool [READ integrates gene expression neighbor (RINGENE)] for genes with similarities in expression profiling.
Figures

References
-
- The RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group Phase II Team and The FANTOM Consortium (2001) Functional annotation of a full-length mouse cDNA collection. Nature, 409, 685–690. - PubMed
-
- Miki R., Kadota,K., Bono,H., Mizuno,Y., Tomaru,Y., Carninci,P., Itoh,M., Shibata,K., Kawai,J., Konno,H. et al. (2001) Delineating developmental and metabolic pathways in vivo by expression profiling using the RIKEN set of 18,816 full-length enriched mouse cDNA arrays. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 2199–2204. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kadota K., Miki,R., Bono,H., Shimizu,K., Okazaki,Y. and Hayashizaki,Y. (2001) Preprocessing implementation for microarray (PRIM): an efficient method for processing cDNA microarray data. Physiol. Genomics, 4, 183–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

