Functional studies of Ycf3: its role in assembly of photosystem I and interactions with some of its subunits
- PMID: 11752384
- PMCID: PMC139485
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010253
Functional studies of Ycf3: its role in assembly of photosystem I and interactions with some of its subunits
Abstract
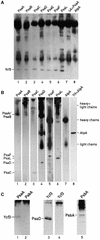
The Ycf3 protein is essential for the accumulation of the photosystem I (PSI) complex and acts at a post-translational level. The sequence of Ycf3 is conserved in cyanobacteria, algae, and plants and contains three tetratrico-peptide repeats (TPR). TPRs have been shown to function as sites for protein-protein interactions. The mutations Y95A/Y96A and Y142A/W143A in the second and third TPR repeats lead to a modest decrease of PSI, but they prevent photoautotrophic growth and cause enhanced light sensitivity even though the accumulated PSI complex is fully functional. This phenotype can be reversed under anaerobic conditions and appears to be the result of photooxidative damage. A temperature-sensitive ycf3 mutant, generated by random mutagenesis of a conserved region near the N-terminal end of Ycf3, was used in temperature-shift experiments to show that Ycf3 is required for PSI assembly but not for its stability. Immunoblot analysis of thylakoid membranes separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoprecipitations shows that Ycf3 interacts directly with the PSI subunits PsaA and PsaD, but not with subunits from other photosynthetic complexes. Thus, Ycf3 appears to act as a chaperone that interacts directly and specifically with at least two of the PSI subunits during assembly of the PSI complex.
Figures




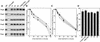




Similar articles
-
The chloroplast ycf3 and ycf4 open reading frames of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are required for the accumulation of the photosystem I complex.EMBO J. 1997 Oct 15;16(20):6095-104. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.20.6095. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9321389 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of four auxiliary factors is required for the assembly of photosystem I reaction center subcomplex.Plant J. 2021 May;106(4):1075-1086. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15220. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Plant J. 2021. PMID: 33655619
-
Characterization of the cyanobacterial ycf37: mutation decreases the photosystem I content.Biochem J. 2001 Jul 1;357(Pt 1):211-6. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3570211. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11415451 Free PMC article.
-
The photosystem I assembly apparatus consisting of Ycf3-Y3IP1 and Ycf4 modules.Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 22;9(1):2439. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04823-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29934511 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplast site-directed mutagenesis of photosystem I in Chlamydomonas: electron transfer reactions and light sensitivity.Biochimie. 2000 Jun-Jul;82(6-7):635-45. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(00)00604-0. Biochimie. 2000. PMID: 10946112 Review.
Cited by
-
The plastid genome-encoded Ycf4 protein functions as a nonessential assembly factor for photosystem I in higher plants.Plant Physiol. 2012 Jun;159(2):579-91. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.196642. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22517411 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory factors for the assembly of thylakoid membrane protein complexes.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Dec 19;367(1608):3420-9. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0065. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23148269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thylakoid membrane proteomics.Photosynth Res. 2003;78(3):265-77. doi: 10.1023/B:PRES.0000006828.65688.0d. Photosynth Res. 2003. PMID: 16245055
-
Unlocking the Complete Chloroplast Genome of a Native Tree Species from the Amazon Basin, Capirona (Calycophyllum Spruceanum, Rubiaceae), and Its Comparative Analysis with Other Ixoroideae Species.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;13(1):113. doi: 10.3390/genes13010113. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052453 Free PMC article.
-
CO-EXPRESSED WITH PSI ASSEMBLY1 (CEPA1) is a photosystem I assembly factor in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2024 Oct 3;36(10):4179-4211. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae042. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38382089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asada, K. (1994). Mechanisms for scavenging reactive molecules generated in chloroplasts under light stress. In Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to the Field, N.R. Baker and J.R. Bowyer, eds (Oxford, UK: BIOS Scientific Publishers), pp. 129–142.
-
- Asada, K. (1996). Radical production and scavenging in the chloroplast. In Advances in Photosynthesis, N.R. Baker, ed (Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers), pp. 123–150.
-
- Barber, J., and Andersson, B. (1992). Too much of a good thing: Light can be bad for photosynthesis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17, 61–66. - PubMed
-
- Bartsevich, V.V., and Pakrasi, H.B. (1997). Molecular identification of a novel protein that regulates biogenesis of photosystem I, a membrane protein complex. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 6382–6387. - PubMed
-
- Bassi, R., Soen, S.Y., Frank, G., Zuber, H., and Rochaix, J.-D. (1992). Characterization of chlorophyll a/b proteins of photosystem I from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 25714–25721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

