The ATP binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) modulates the development of aortic atherosclerosis in C57BL/6 and apoE-knockout mice
- PMID: 11752403
- PMCID: PMC117573
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.012587699
The ATP binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) modulates the development of aortic atherosclerosis in C57BL/6 and apoE-knockout mice
Abstract
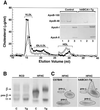
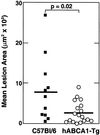
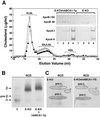
Identification of mutations in the ABCA1 transporter (ABCA1) as the genetic defect in Tangier disease has generated interest in modulating atherogenic risk by enhancing ABCA1 gene expression. To investigate the role of ABCA1 in atherogenesis, we analyzed diet-induced atherosclerosis in transgenic mice overexpressing human ABCA1 (hABCA1-Tg) and spontaneous lesion formation in hABCA1-Tg x apoE-knockout (KO) mice. Overexpression of hABCA1 in C57BL/6 mice resulted in a unique anti-atherogenic profile characterized by decreased plasma cholesterol (63%), cholesteryl ester (63%), free cholesterol (67%), non-high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol (53%), and apolipoprotein (apo) B (64%) but markedly increased HDL-cholesterol (2.8-fold), apoA-I (2.2-fold), and apoE (2.8-fold) levels. These beneficial changes in the lipid profile led to significantly lower (65%) aortic atherosclerosis in hABCA1-Tg mice. In marked contrast, ABCA1 overexpression had a minimal effect on the plasma lipid profile of apoE-KO mice and resulted in a 2- to 2.6-fold increase in aortic lesion area. These combined results indicate that overexpression of ABCA1 in C57BL/6 mice on a high cholesterol diet results in an atheroprotective lipoprotein profile and decreased atherosclerosis, and thus provide previously undocumented in vivo evidence of an anti-atherogenic role for the ABCA1 transporter. In contrast, overexpression of ABCA1 in an apoE-KO background led to increased atherosclerosis, further substantiating the important role of apoE in macrophage cholesterol metabolism and atherogenesis. In summary, these results establish that, in the presence of apoE, overexpression of ABCA1 modulates HDL as well as apoB-containing lipoprotein metabolism and reduces atherosclerosis in vivo, and indicate that pharmacological agents that will increase ABCA1 expression may reduce atherogenic risk in humans.
Figures

References
-
- Gordon D J, Rifkind B M. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1311–1316. - PubMed
-
- Miller N E. Am Heart J. 1987;113:589–597. - PubMed
-
- Gordon D J, Probstfield J L, Garrison R J, Neaton J D, Castelli W P, Knoke J D, Jr, Jacobs D R, Jr, Bangdiwala S, Tyroler H A. Circulation. 1989;79:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Glomset J A. J Lipid Res. 1968;9:155–167. - PubMed
-
- Fielding C J, Fielding P E. J Lipid Res. 1995;36:211–228. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

