Trends of measured climate forcing agents
- PMID: 11752424
- PMCID: PMC64935
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261553698
Trends of measured climate forcing agents
Abstract
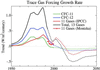
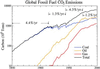
The growth rate of climate forcing by measured greenhouse gases peaked near 1980 at almost 5 W/m(2) per century. This growth rate has since declined to approximately 3 W/m(2) per century, largely because of cooperative international actions. We argue that trends can be reduced to the level needed for the moderate "alternative" climate scenario ( approximately 2 W/m(2) per century for the next 50 years) by means of concerted actions that have other benefits, but the forcing reductions are not automatic "co-benefits" of actions that slow CO(2) emissions. Current trends of climate forcings by aerosols remain very uncertain. Nevertheless, practical constraints on changes in emission levels suggest that global warming at a rate +0.15 +/- 0.05 degrees C per decade will occur over the next several decades.
Figures





References
-
- Hansen J, Ruedy R, Sato M, Imhoff M, Lawrence W, Easterling D, Peterson T, Karl T. J Geophys Res. 2001;106:23947–23963.
-
- Jones P D, New M, Parker D E, Martin S, Rigor I G. Rev Geophys. 1999;37:173–199.
-
- Houghton J T, Ding Y, Griggs D J, Noguer M, van der Linden P J, Dai X, Maskell K, Johnson C A, editors. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2001. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge Univ. Press; 2001.
-
- Hansen J, Sato M, Ruedy R. J Geophys Res. 1997;102:6831–6864.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

