Combining multiple structure and sequence alignments to improve sequence detection and alignment: application to the SH2 domains of Janus kinases
- PMID: 11752426
- PMCID: PMC64938
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.011577898
Combining multiple structure and sequence alignments to improve sequence detection and alignment: application to the SH2 domains of Janus kinases
Abstract
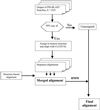
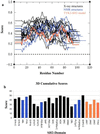
In this paper, an approach is described that combines multiple structure alignments and multiple sequence alignments to generate sequence profiles for protein families. First, multiple sequence alignments are generated from sequences that are closely related to each sequence of known three-dimensional structure. These alignments then are merged through a multiple structure alignment of family members of known structure. The merged alignment is used to generate a Hidden Markov Model for the family in question. The Hidden Markov Model can be used to search for new family members or to improve alignments for distantly related family members that already have been identified. Application of a profile generated for SH2 domains indicates that the Janus family of nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases contains SH2 domains. This conclusion is strongly supported by the results of secondary structure-prediction programs, threading calculations, and the analysis of comparative models generated for these domains. One of the Janus kinases, human TYK2, has an SH2 domain that contains a histidine instead of the conserved arginine at the key phosphotyrosine-binding position, betaB5. Calculations of the pK(a) values of the betaB5 arginines in a number of SH2 domains and of the betaB5 histidine in a homology model of TYK2 suggest that this histidine is likely to be neutral around pH 7, thus indicating that it may have lost the ability to bind phosphotyrosine. If this indeed is the case, TYK2 may contain a domain with an SH2 fold that has a modified binding specificity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Using CLUSTAL for multiple sequence alignments.Methods Enzymol. 1996;266:383-402. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)66024-8. Methods Enzymol. 1996. PMID: 8743695
-
Computational and functional analysis of the putative SH2 domain in Janus Kinases.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Nov 11;278(1):175-82. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3757. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 11071870
-
Classification and Lineage Tracing of SH2 Domains Throughout Eukaryotes.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1555:59-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6762-9_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28092027
-
Recognition of a high-affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide by the Src homology-2 domain of p56lck.Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):87-91. doi: 10.1038/362087a0. Nature. 1993. PMID: 7680435
-
Tyrosine kinase signalling pathways.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994;24:303-22. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994. PMID: 8983084 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural genomics: computational methods for structure analysis.Protein Sci. 2003 Sep;12(9):1813-21. doi: 10.1110/ps.0242903. Protein Sci. 2003. PMID: 12930981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of an ideal-like fingerprint for a protein fold using overlapped conserved residues based approach.Sci Rep. 2014 Jul 10;4:5643. doi: 10.1038/srep05643. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25008052 Free PMC article.
-
patGPCR: a multitemplate approach for improving 3D structure prediction of transmembrane helices of G-protein-coupled receptors.Comput Math Methods Med. 2013;2013:486125. doi: 10.1155/2013/486125. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Comput Math Methods Med. 2013. PMID: 23554839 Free PMC article.
-
Template-based protein structure modeling.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;673:73-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-842-3_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20835794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of Protein Tertiary Structure via Regularized Template Classification Techniques.Molecules. 2020 May 26;25(11):2467. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112467. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32466409 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

