Partial purification and identification of GDP-mannose 3",5"-epimerase of Arabidopsis thaliana, a key enzyme of the plant vitamin C pathway
- PMID: 11752432
- PMCID: PMC64946
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.011578198
Partial purification and identification of GDP-mannose 3",5"-epimerase of Arabidopsis thaliana, a key enzyme of the plant vitamin C pathway
Abstract
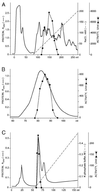
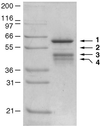
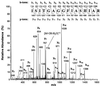
The first step in the biosynthetic pathway of vitamin C in plants is the formation, at the level of sugar nucleotide, of l-galactosyl residues, catalyzed by a largely unknown GDP-d-mannose 3",5"-epimerase. By using combined conventional biochemical and mass spectrometry methods, we obtained a highly purified preparation of GDP-d-mannose 3",5"-epimerase from an Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspension. The native enzyme is an 84-kDa dimer, composed of two apparently identical subunits. In-gel tryptic digestion of the enzyme subunit, followed by peptide sequencing and a blast search, led to the identification of the epimerase gene. The closest homolog of the plant epimerase is the BlmG gene product of Streptomyces sp., a putative NDP-d-mannose 5"-epimerase. The plant GDP-d-mannose 3",5"-epimerase is, to our knowledge, a novel member of the extended short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family. The enzyme was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli cells.
Figures
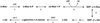

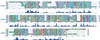
References
-
- Smirnoff N, Wheeler G L. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2000;19:267–290.
-
- Nishikimi M, Fukuyama R, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Yagi K. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:13685–13688. - PubMed
-
- Nishikimi M, Yagi K. Subcell Biochem. 1996;25:17–39. - PubMed
-
- Davey M W, Van Montagu M, Inzé D, Sanmartin M, Kanellis A, Smirnoff N, Benzie I J J, Strain J J, Favell D, Fletcher J. J Sci Food Agric. 2000;80:825–860.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

