The Abl-related gene (Arg) nonreceptor tyrosine kinase uses two F-actin-binding domains to bundle F-actin
- PMID: 11752434
- PMCID: PMC64950
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.251249298
The Abl-related gene (Arg) nonreceptor tyrosine kinase uses two F-actin-binding domains to bundle F-actin
Abstract
Abl family nonreceptor tyrosine kinases regulate cellular morphogenesis and motility through functional interactions with the actin cytoskeleton. Although Abl family kinases are known to contain filamentous (F)-actin-binding domains at their C termini, it is unclear how Abl family kinases regulate the structure and/or function of the actin cytoskeleton. We show here that the Abl-related kinase Arg binds with positive cooperativity to F-actin in vitro with binding saturating at a ratio of one Arg/two actin molecules. Measurements of the F-actin-binding properties of Arg deletion mutants led to the identification of a second, previously uncharacterized internal F-actin-binding domain in Arg. Purified Arg can bundle F-actin in vitro, and this bundling activity requires both F-actin-binding domains. An Arg-yellow fluorescent protein fusion protein can induce the formation of actin-rich structures at the lamellipodia of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Both of Arg's F-actin-binding domains are necessary and sufficient for the formation of these actin-rich structures. Together, our data suggest that Arg can use its F-actin-bundling activity to directly regulate actin cytoskeletal structure in vivo.
Figures
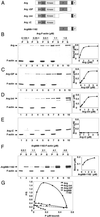
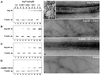

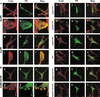
Comment in
-
Creating a niche in the cytoskeleton: Actin reorganization by a protein kinase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 18;98(26):14745-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011601598. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11752415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The Abl-related gene (Arg) requires its F-actin-microtubule cross-linking activity to regulate lamellipodial dynamics during fibroblast adhesion.J Cell Biol. 2004 May 10;165(3):407-19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200308055. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15138293 Free PMC article.
-
The Arg non-receptor tyrosine kinase modifies F-actin structure.J Mol Biol. 2005 Feb 18;346(2):565-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.11.078. Epub 2004 Dec 23. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15670605
-
The COOH terminus of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase contains distinct F- and G-actin binding domains with bundling activity.J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(3):325-40. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.3.325. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8294516 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of F-actin-dependent processes by the Abl family of tyrosine kinases.J Cell Sci. 2003 Jul 1;116(Pt 13):2613-26. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00622. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12775773 Review.
-
Arg kinase signaling in dendrite and synapse stabilization pathways: memory, cocaine sensitivity, and stress.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;45(11):2496-500. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.07.018. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23916785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Abl2/Abl-related gene stabilizes actin filaments, stimulates actin branching by actin-related protein 2/3 complex, and promotes actin filament severing by cofilin.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 13;290(7):4038-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.608117. Epub 2014 Dec 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25540195 Free PMC article.
-
Neurabin/protein phosphatase-1 complex regulates dendritic spine morphogenesis and maturation.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 May;16(5):2349-62. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1054. Epub 2005 Mar 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15743906 Free PMC article.
-
Creating a niche in the cytoskeleton: Actin reorganization by a protein kinase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 18;98(26):14745-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011601598. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11752415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Integrin-mediated dendrite branch maintenance requires Abelson (Abl) family kinases.J Neurosci. 2005 Jun 29;25(26):6105-18. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1432-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15987940 Free PMC article.
-
Abelson family tyrosine kinases regulate the function of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic synapses on autonomic neurons.Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Jul;80(1):97-109. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.071308. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21502378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gertler F B, Bennett R L, Clark M J, Hoffmann F M. Cell. 1989;58:103–113. - PubMed
-
- Giniger E. Neuron. 1998;20:667–681. - PubMed
-
- Wills Z, Bateman J, Korey C A, Comer A, Van Vactor D. Neuron. 1999;22:301–312. - PubMed
-
- Wills Z, Marr L, Zinn K, Goodman C S, Van Vactor D. Neuron. 1999;22:291–299. - PubMed
-
- Zukerberg L R, Patrick G N, Nikolic M, Humbert S, Wu C L, Lanier L M, Gertler F B, Vidal M, Van Etten R A, Tsai L H. Neuron. 2000;26:633–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

