Elevated expression of axin2 and hnkd mRNA provides evidence that Wnt/beta -catenin signaling is activated in human colon tumors
- PMID: 11752446
- PMCID: PMC64968
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261574498
Elevated expression of axin2 and hnkd mRNA provides evidence that Wnt/beta -catenin signaling is activated in human colon tumors
Abstract
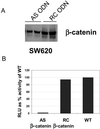
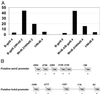
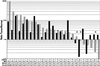
Genetic studies have identified mutations in key regulators of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in a variety of cancers, most frequently in colon cancers. However, whether the pathway is activated in clinical cancer samples is not easily determined, and therefore it is useful to find markers that could be surrogates to show activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Gene expression profiles were analyzed in SW620, a colon cancer cell line in which beta-catenin levels are stabilized as a consequence of truncated adenomatous polyposis coli and were compared with profiles of the same cells transfected with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Treatment of cells with beta-catenin antisense oligodeoxynucleotides resulted in a decrease in the levels of axin2 and human naked cuticle (hnkd) mRNAs. Interestingly, the proteins encoded by both of these mRNAs are known inhibitors of the beta-catenin pathway. In 30 human cell lines derived from different origins, axin2 and hnkd were expressed only in human colon cancer cell lines that are known to have activating mutations in the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Further, levels of both axin2 and hnkd mRNA were also found to be elevated in about 65% of laser microdissected cells from human colon tumors compared with laser microdissected cells of normal morphology from the same patient samples. The increased expression of axin2 and hnkd correlated with truncations in adenomatous polyposis coli in the same patient samples. These results reveal that it is possible to detect activation of a carcinogenic pathway in human cancer samples with specific markers.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel colon cancer cell lines leading to better understanding of the diversity of respective primary cancers.Oncogene. 2002 Jul 11;21(30):4646-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205577. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12096341
-
beta-Catenin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer.Cancer Res. 2003 Jun 15;63(12):3145-53. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12810642
-
AXIN1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas, and growth suppression in cancer cells by virus-mediated transfer of AXIN1.Nat Genet. 2000 Mar;24(3):245-50. doi: 10.1038/73448. Nat Genet. 2000. PMID: 10700176
-
Catenins, Wnt signaling and cancer.Bioessays. 2000 Nov;22(11):961-5. doi: 10.1002/1521-1878(200011)22:11<961::AID-BIES1>3.0.CO;2-T. Bioessays. 2000. PMID: 11056471 Review.
-
Regulation of beta-catenin signaling in the Wnt pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Feb 16;268(2):243-8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1860. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 10679188 Review.
Cited by
-
The NKD1/Rac1 feedback loop regulates the invasion and migration ability of hepatocarcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2016 May 27;6:26971. doi: 10.1038/srep26971. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27231134 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt antagonist sFRP1 is downregulated in premalignant large bowel adenomas.Br J Cancer. 2006 Mar 27;94(6):922-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602967. Br J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16523202 Free PMC article.
-
Viable mice with compound mutations in the Wnt/Dvl pathway antagonists nkd1 and nkd2.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;27(12):4454-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00133-07. Epub 2007 Apr 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17438140 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-catenin signaling negatively regulates intermediate progenitor population numbers in the developing cortex.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 25;5(8):e12376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012376. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20811503 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of NKD1 increases the invasive potential of non-small-cell lung cancer and correlates with a poor prognosis.BMC Cancer. 2011 May 20;11:186. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-186. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21599923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polakis P. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, Albertsen H, Joslyn G, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, et al. Cell. 1991;66:589–600. - PubMed
-
- Kinzler K W, Nilbert M C, Su L K, Vogelstein B, Bryan T M, Levy D B, Smith K J, Preisinger A C, Hedge P, McKechnie D, et al. Science. 1991;253:661–665. - PubMed
-
- Satoh S, Daigo Y, Furukawa Y, Kato T, Miwa N, Nishiwaki T, Kawasoe T, Ishiguro H, Fujita M, Tokino T, et al. Nat Genet. 2000;24:245–250. - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Dong X, Mai M, Seelan R S, Taniguchi K, Krishnadath K K, Halling K C, Cunningham J M, Boardman L A, Qian C, et al. Nat Genet. 2000;26:146–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

