Positional cloning of the combined hyperlipidemia gene Hyplip1
- PMID: 11753387
- PMCID: PMC2846781
- DOI: 10.1038/ng811
Positional cloning of the combined hyperlipidemia gene Hyplip1
Abstract
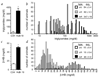
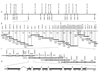
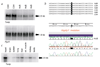
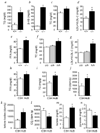
Familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCHL, MIM-144250) is a common, multifactorial and heterogeneous dyslipidemia predisposing to premature coronary artery disease and characterized by elevated plasma triglycerides, cholesterol, or both. We identified a mutant mouse strain, HcB-19/Dem (HcB-19), that shares features with FCHL, including hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, elevated plasma apolipoprotein B and increased secretion of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. The hyperlipidemia results from spontaneous mutation at a locus, Hyplip1, on distal mouse chromosome 3 in a region syntenic with a 1q21-q23 FCHL locus identified in Finnish, German, Chinese and US families. We fine-mapped Hyplip1 to roughly 160 kb, constructed a BAC contig and sequenced overlapping BACs to identify 13 candidate genes. We found substantially decreased mRNA expression for thioredoxin interacting protein (Txnip). Sequencing of the critical region revealed a Txnip nonsense mutation in HcB-19 that is absent in its normolipidemic parental strains. Txnip encodes a cytoplasmic protein that binds and inhibits thioredoxin, a major regulator of cellular redox state. The mutant mice have decreased CO2 production but increased ketone body synthesis, suggesting that altered redox status down-regulates the citric-acid cycle, sparing fatty acids for triglyceride and ketone body production. These results reveal a new pathway of potential clinical significance that contributes to plasma lipid metabolism.
Figures

References
-
- Genest JJ, Jr, et al. Familial lipoprotein disorders in patients with premature coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1992;85:2025–2033. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM, Chait A, Brunzell JD. Familial combined hyperlipidemia workshop. Arteriosclerosis. 1987;7:203–207.
-
- Nikkila EA, Aro A. Family study of serum lipids and lipoproteins in coronary heart-disease. Lancet. 1973;1:954–959. - PubMed
-
- Castellani LW, et al. Mapping a gene for combined hyperlipidaemia in a mutant mouse strain. Nature Genet. 1998;18:374–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

