Implication of a novel multiprotein Dam1p complex in outer kinetochore function
- PMID: 11756468
- PMCID: PMC2199314
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200109063
Implication of a novel multiprotein Dam1p complex in outer kinetochore function
Abstract
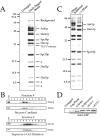
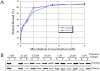
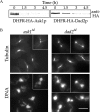
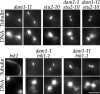
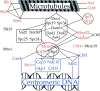
Dam1p, Duo1p, and Dad1p can associate with each other physically and are required for both spindle integrity and kinetochore function in budding yeast. Here, we present our purification from yeast extracts of an approximately 245 kD complex containing Dam1p, Duo1p, and Dad1p and Spc19p, Spc34p, and the previously uncharacterized proteins Dad2p and Ask1p. This Dam1p complex appears to be regulated through the phosphorylation of multiple subunits with at least one phosphorylation event changing during the cell cycle. We also find that purified Dam1p complex binds directly to microtubules in vitro with an affinity of approximately 0.5 microM. To demonstrate that subunits of the Dam1p complex are functionally important for mitosis in vivo, we localized Spc19-green fluorescent protein (GFP), Spc34-GFP, Dad2-GFP, and Ask1-GFP to the mitotic spindle and to kinetochores and generated temperature-sensitive mutants of DAD2 and ASK1. These and other analyses implicate the four newly identified subunits and the Dam1p complex as a whole in outer kinetochore function where they are well positioned to facilitate the association of chromosomes with spindle microtubules.
Figures

References
-
- Ayscough, K.R., and D.G. Drubin. 1998. Immunofluorescence microscopy of yeast cells. Cell Biology: A Laboratory Handbook. Vol. 2. J. Celis, editor. Academic Press, Inc., New York. 477–485.
-
- Dohmen, R.J., P. Wu, and A. Varshavsky. 1994. Heat-inducible degron: a method for constructing temperature-sensitive mutants. Science. 263:1273–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

