Cytoplasmic dynein/dynactin drives kinetochore protein transport to the spindle poles and has a role in mitotic spindle checkpoint inactivation
- PMID: 11756470
- PMCID: PMC2199338
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200105093
Cytoplasmic dynein/dynactin drives kinetochore protein transport to the spindle poles and has a role in mitotic spindle checkpoint inactivation
Abstract
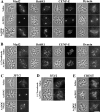
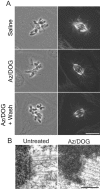
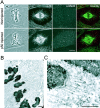
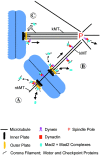
We discovered that many proteins located in the kinetochore outer domain, but not the inner core, are depleted from kinetochores and accumulate at spindle poles when ATP production is suppressed in PtK1 cells, and that microtubule depolymerization inhibits this process. These proteins include the microtubule motors CENP-E and cytoplasmic dynein, and proteins involved with the mitotic spindle checkpoint, Mad2, Bub1R, and the 3F3/2 phosphoantigen. Depletion of these components did not disrupt kinetochore outer domain structure or alter metaphase kinetochore microtubule number. Inhibition of dynein/dynactin activity by microinjection in prometaphase with purified p50 "dynamitin" protein or concentrated 70.1 anti-dynein antibody blocked outer domain protein transport to the spindle poles, prevented Mad2 depletion from kinetochores despite normal kinetochore microtubule numbers, reduced metaphase kinetochore tension by 40%, and induced a mitotic block at metaphase. Dynein/dynactin inhibition did not block chromosome congression to the spindle equator in prometaphase, or segregation to the poles in anaphase when the spindle checkpoint was inactivated by microinjection with Mad2 antibodies. Thus, a major function of dynein/dynactin in mitosis is in a kinetochore disassembly pathway that contributes to inactivation of the spindle checkpoint.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microtubule-dependent changes in assembly of microtubule motor proteins and mitotic spindle checkpoint proteins at PtK1 kinetochores.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jul;12(7):1995-2009. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.7.1995. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11451998 Free PMC article.
-
Dynein/Dynactin-mediated transport of kinetochore components off kinetochores and onto spindle poles induced by nordihydroguaiaretic acid.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 28;6(1):e16494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016494. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21305043 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic dynein participates in meiotic checkpoint inactivation in mouse oocytes by transporting cytoplasmic mitotic arrest-deficient (Mad) proteins from kinetochores to spindle poles.Reproduction. 2007 Apr;133(4):685-95. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.01167. Reproduction. 2007. PMID: 17504913
-
Mechanisms of Chromosome Congression during Mitosis.Biology (Basel). 2017 Feb 17;6(1):13. doi: 10.3390/biology6010013. Biology (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28218637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merotelic kinetochores in mammalian tissue cells.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Mar 29;360(1455):553-68. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1610. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15897180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Energy restriction causes metaphase delay and chromosome mis-segregation in cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2021 Jun;20(12):1195-1208. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1930679. Epub 2021 May 28. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34048314 Free PMC article.
-
Multimerization of a disordered kinetochore protein promotes accurate chromosome segregation by localizing a core dynein module.J Cell Biol. 2024 Mar 4;223(3):e202211122. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202211122. Epub 2024 Jan 5. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38180477 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule binding by KNL-1 contributes to spindle checkpoint silencing at the kinetochore.J Cell Biol. 2012 Feb 20;196(4):469-82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201111107. Epub 2012 Feb 13. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22331849 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring spindle orientation: Spindle position checkpoint in charge.Cell Div. 2010 Dec 11;5:28. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-5-28. Cell Div. 2010. PMID: 21143992 Free PMC article.
-
Spindle checkpoint silencing: ensuring rapid and concerted anaphase onset.F1000 Biol Rep. 2010 Jul 22;2:55. doi: 10.3410/B2-55. F1000 Biol Rep. 2010. PMID: 21173869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banks, J.D., and R. Heald. 2001. Chromosome movement: Dynein-out at the kinetochore. Curr. Biol. 11: R128–R131. - PubMed
-
- Basto, R., R. Gomes, and R.E. Karess. 2000. Rough Deal and Zw10 are required for the metaphase checkpoint in Drosophila. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:939–943. - PubMed
-
- Bershadsky, A.D., and V.I. Gelfand. 1983. Role of ATP in the regulation and stability of cytoskeletal structures. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 5:173–187. - PubMed
-
- Canman, J.C., D.B. Hoffman, and E.D. Salmon. 2000. The role of pre-and post-anaphase microtubules in the cytokinesis phase of the cell cycle. Curr. Biol. 10:611–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

